Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Distinguish between a conductor, a semiconductor and an insulator on the basis of energy band diagrams.
Solution
The energy-band diagram of a conductor is represented as
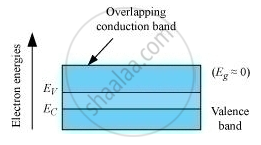
The energy-band diagram of a semiconductor is represented as
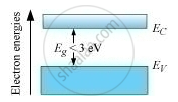
The energy-band diagram of an insulator is represented as

APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Distinguish between a metal and an insulator on the basis of energy band diagrams ?
How many 1s energy states are present in one mole of sodium vapour? Are they all filled in normal conditions? How many 3s energy states are present in one mole of sodium vapour? Are they all filled in normal conditions?
Electric conduction in a semiconductor takes place due to
A p-type semiconductor is
In a semiconductor,
(a) there are no free electrons at 0 K
(b) there are no free electrons at any temperature
(c) the number of free electrons increases with temperature
(d) the number of free electrons is less than that in a conductor.
A semiconductor is doped with a donor impurity.
The conductivity of an intrinsic semiconductor depends on temperature as σ = σ0e−ΔE/2kT, where σ0 is a constant. Find the temperature at which the conductivity of an intrinsic germanium semiconductor will be double of its value at T = 300 K. Assume that the gap for germanium is 0.650 eV and remains constant as the temperature is increased.
(Use Planck constant h = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, Boltzmann constant k = 8·62 × 10-5 eV/K.)
The energy of a hydrogen atom in the ground state is −13.6 eV. The energy of a He+ ion in the first excited state will be:
In a common-base circuit calculate the change in the base current if that in the emitter current is αmA and a = 0.98
The energy required by an electron to jump the forbidden band in silicon at room temperature is about ______.
