Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
How many 1s energy states are present in one mole of sodium vapour? Are they all filled in normal conditions? How many 3s energy states are present in one mole of sodium vapour? Are they all filled in normal conditions?
Solution
For sodium, the atomic number is 11. The electronic configuration of sodium is 1s2 2s22p6 3s1.
One sodium atom has 11 electrons. Thus, if the sodium crystals consist of N atoms, the total number of electrons will be 11 N. We know that for each atom, there are two states in the energy level 1s. Thus, the sodium crystal will have 2 N states for 1s energy level. Similarly, the number of states in 3s energy level will also be 2 N. 1s state is filled under normal condition. But the 3s state has only one electron per sodium atom, so the 3s band will be half-filled.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Distinguish between a metal and an insulator on the basis of energy band diagrams ?
In semiconductors, thermal collisions are responsible for taking a valence electron to the conduction band. Why does the number of conduction electrons not go on increasing with time as thermal collisions continuously take place?
What is the resistance of an intrinsic semiconductor at 0 K?
An electric field is applied to a semiconductor. Let the number of charge carries be nand the average drift speed by v. If the temperature is increased,
Let np and ne be the number of holes and conduction electrons in an intrinsic semiconductor.
A p-type semiconductor is
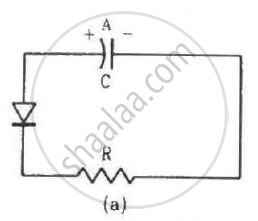
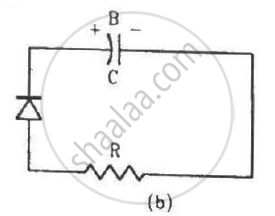
Two identical capacitors A and B are charged to the same potential V and are connected in two circuits at t = 0 as shown in figure. The charges on the capacitors at a time t = CRare, respectively,
The impurity atoms with which pure silicon may be doped to make it a p-type semiconductor are those of
(a) phosphorus
(b) boron
(c) antimony
(d) aluminium.
In a pure semiconductor, the number of conduction election 6 × 1019 per cubic metre. How many holes are there in a sample of size 1 cm × 1 mm?
The band gap for silicon is 1.1 eV. (a) Find the ratio of the band gap to kT for silicon at room temperature 300 K. (b) At what temperature does this ratio become one tents of the value at 300 K? (Silicon will not retain its structure at these high temperatures.)
(Use Planck constant h = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, Boltzmann constant k = 8·62 × 10-5 eV/K.)
The band gap between the valence and the conduction bands in zinc oxide (ZnO) is 3.2 eV. Suppose an electron in the conduction band combines with a hole in the valence band and the excess energy is released in the form of electromagnetic radiation. Find the maximum wavelength that can be emitted in this process.
Find the maximum wavelength of electromagnetic radiation which can create a hole-electron pair in germanium. The band gap in germanium is 0.65 eV.
(Use Planck constant h = 4.14 × 10-15 eV-s, Boltzmann constant k = 8·62 × 10-5 eV/K.)
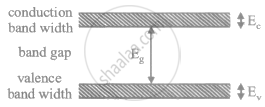
What is forbidden band?
Two radioactive substances A and B have decay constants 3λ and λ respectively. At t = 0 they have the same number of nuclei. The ratio of the number of nuclei of A to those of B will be `1/"e"` after a time interval:
If the lattice constant of this semiconductor is decreased, then which of the following is correct?
The energy of a hydrogen atom in the ground state is −13.6 eV. The energy of a He+ ion in the first excited state will be:
Draw the energy band diagrams for conductors, semiconductors and insulators. Which band determines the electrical conductivity of a solid? How is the electrical conductivity of a semiconductor affected with rise in its temperature? Explain.
With reference to semiconductor physics, answer the following question.
What is meant by “Forbidden band" of energy levels?
