Science (English Medium)
Academic Year: 2009-2010
Date: March 2010
Advertisements
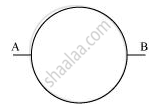
A plot of magnetic flux (Φ) versus current (I) is shown in the figure for two inductors A and Β. Which of the two has larger value of self inductance?

Chapter: [0.06] Electromagnetic Induction
Figure shows three point charges +2q, −q and + 3q. Two charges + 2q and −q are enclosed within a surface ‘S’. What is the electric flux due to this configuration through the surface ‘S’?
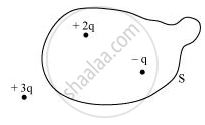
Chapter: [0.01] Electric Charges and Fields
In which orientation, a dipole placed in a uniform electric field is in (i) stable, (ii) unstable equilibrium?
Chapter: [0.01] Electric Charges and Fields
Which part of electromagnetic spectrum is used in radar systems?
Chapter: [0.08] Electromagnetic Waves
Calculate the speed of light in a medium whose critical angle is 30° ?
Chapter: [0.09] Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
A glass lens of refractive index 1.45 disappears when immersed in a liquid. What is the value of refractive index of the liquid?
Chapter: [0.09] Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
Write the expression for Bohr’s radius in hydrogen atom ?
Chapter: [0.12] Atoms
A wire of resistance 8R is bent in the form of a circle. What is the effective resistance between the ends of a diameter AB?
Chapter:
Explain the function of a repeater in a communication system.
Chapter: [0.15] Communication Systems
Write two characteristics of a material used for making permanent magnets ?
Chapter: [0.05] Magnetism and Matter
Why is the core of an electromagnet made of ferromagnetic materials?
Chapter: [0.05] Magnetism and Matter
Draw magnetic field line when a (i) diamagnetic, (ii) paramagnetic substance is placed in an external magnetic field. Which magnetic property distinguishes this behaviour of the field line due to the substances?
Chapter: [0.05] Magnetism and Matter
What is the range of frequencies used in satellite communication?
Chapter: [0.15] Communication Systems
What is common between these waves and light waves?
Chapter: [0.15] Communication Systems
A coil Q is connected to low voltage bulb B and placed near another coil P as shown in the figure. Give reasons to explain the following observations:
(a) The bulb ‘B’ lights
(b) Bulb gets dimmer if the coil Q is moved towards left.
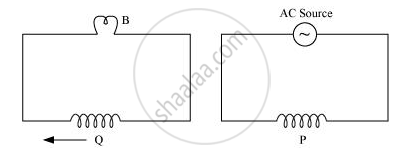
Chapter: [0.07] Alternating Current
Find the radius of curvature of the convex surface of a plano-convex lens, whose focal length is 0.3 m and the refractive index of the material of the lens is 1.5.
Chapter: [0.09] Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
An electron is accelerated through a potential difference of 64 volts. What is the de-Broglie wavelength associated with it? To which part of the electromagnetic spectrum does this value of wavelength correspond?
Chapter: [0.11] Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter
Advertisements
Out of blue and red light which is deviated more by a prism? Give reason.
Chapter: [0.09] Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
Give the formula that can be used to determine refractive index of materials of a prism in minimum deviation condition ?
Chapter: [0.09] Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
Plot a graph showing the variation of stopping potential with the frequency of incident radiation for two different photosensitive materials having work functions W1 and W2 (W1 > W2). On what factors does the (i) slope and (ii) intercept of the lines depend?
Chapter: [0.03] Current Electricity
Draw the circuit diagram of an illuminated photodiode in reverse bias. How is photodiode used to measure light intensity?
Chapter: [0.14] Semiconductor Electronics - Materials, Devices and Simple Circuits
A heavy nucleus X of mass number 240 and binding energy per nucleon 7.6 MeV is split into two fragments Y and Z of mass numbers 110 and 130. The binding energy of nucleons in Y and Z is 8.5 MeV per nucleon. Calculate the energy Q released per fission in MeV.
Chapter: [0.13] Nuclei
Depict the equipotential surfaces for a system of two identical positive point charges placed a distance(d) apart?
Chapter: [0.02] Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance
Deduce the expression for the potential energy of a system of two point charges q1 and q2 brought from infinity to the points `vecr_1`and `vecr_2`respectively in the presence of external electric field `vecE`.
Chapter: [0.02] Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance
In a meter bridge, the null point is found at a distance of l1 cm from A. If now a resistance of X is connected in parallel with S, the null point occurs at l2 cm. Obtain a formula for X in terms of l1, l2 and S.

Chapter: [0.03] Current Electricity
What is space wave propagation?
Chapter: [0.15] Communication Systems
Give two examples of communication system which use space wave mode.
A TV tower is 80 m tall. Calculate the maximum distance upto which the signal transmitted from the tower can be received.
Chapter: [0.15] Communication Systems
Define ‘activity’ of a radioactive material and write its S.I. units.
Chapter: [0.13] Nuclei
Plot a graph showing variation of activity of a given radioactive sample with time.
Chapter: [0.13] Nuclei
The sequence of stepwise decay of a radioactive nucleus is
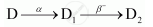
If the atomic number and mass number of D2 are 71 and 176 respectively, what are their corresponding values of D?
Chapter: [0.13] Nuclei
What is an unpolarized light? Explain with the help of suitable ray diagram how an unpolarized light can be polarized by reflection from a transparent medium. Write the expression for Brewster angle in terms of the refractive index of denser medium.
Chapter: [0.1] Wave Optics
Write the principle of working of a potentiometer. Describe briefly, with the help of a circuit diagram, how a potentiometer is used to determine the internal resistance of a given cell.
Chapter: [0.03] Current Electricity
Write the expression for the magnetic moment `vecm`due to a planar square loop of side ‘l’ carrying a steady current I in a vector form.
In the given figure this loop is placed in a horizontal plane near a long straight conductor carrying a steady current I1 at a distance l as shown. Give reason to explain that the loop will experience a net force but no torque. Write the expression for this force acting on the loop.

Chapter: [0.04] Moving Charges and Magnetism
Advertisements
A long straight wire of a circular cross-section of radius ‘a’ carries a steady current ‘I’. The current is uniformly distributed across the cross-section. Apply Ampere’s circuital law to calculate the magnetic field at a point ‘r’ in the region for (i) r < a and (ii) r > a.
Chapter: [0.04] Moving Charges and Magnetism
State the underlying principle of working of a moving coil galvanometer. Write two reasons why a galvanometer can not be used as such to measure current in a given circuit. Name any two factors on which the current sensitivity of a galvanometer depends.
Chapter: [0.04] Moving Charges and Magnetism
A parallel-plate capacitor is charged to a potential difference V by a dc source. The capacitor is then disconnected from the source. If the distance between the plates is doubled, state with reason how the following change:
(i) electric field between the plates
(ii) capacitance, and
(iii) energy stored in the capacitor
Chapter: [0.02] Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance
Explain the formation of depletion layer and potential barrier in a p−n junction.
Chapter: [0.14] Semiconductor Electronics - Materials, Devices and Simple Circuits
In the figure given below the input waveform is converted into the output waveform by a device ‘X’. Name the device and draw its circuit diagram.
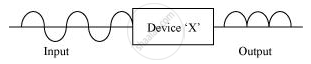
Chapter: [0.14] Semiconductor Electronics - Materials, Devices and Simple Circuits
Identify the logic gate represented by the circuit as shown and write its truth table.
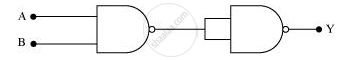
Chapter: [0.14] Semiconductor Electronics - Materials, Devices and Simple Circuits
With the help of circuit diagram explain the working principle of a transistor amplifier as an oscillator.
Chapter: [0.14] Semiconductor Electronics - Materials, Devices and Simple Circuits
Distinguish between a conductor, a semiconductor and an insulator on the basis of energy band diagrams.
Chapter: [0.14] Semiconductor Electronics - Materials, Devices and Simple Circuits
Describe briefly, with the help of a labelled diagram, the basic elements of an A.C. generator.
Chapter: [0.06] Electromagnetic Induction
State A.C. generator underlying principle?
Chapter: [0.06] Electromagnetic Induction
Show diagrammatically how an alternating emf is generated by a loop of wire rotating in a magnetic field. Write the expression for the instantaneous value of the emf induced in the rotating loop.
Chapter: [0.06] Electromagnetic Induction
A series LCR circuit is connected to a source having voltage v = vm sin ωt. Derive the expression for the instantaneous current I and its phase relationship to the applied voltage.
Obtain the condition for resonance to occur. Define ‘power factor’. State the conditions under which it is (i) maximum and (ii) minimum.
Chapter: [0.07] Alternating Current
State Huygens’s principle. Show, with the help of a suitable diagram, how this principle is used to obtain the diffraction pattern by a single slit.
Draw a plot of intensity distribution and explain clearly why the secondary maxima becomes weaker with increasing order (n) of the secondary maxima.
Chapter: [0.1] Wave Optics
Draw a ray diagram to show the working of a compound microscope. Deduce an expression for the total magnification when the final image is formed at the near point.
In a compound microscope, an object is placed at a distance of 1.5 cm from the objective of focal length 1.25 cm. If the eye piece has a focal length of 5 cm and the final image is formed at the near point, estimate the magnifying power of the microscope.
Chapter: [0.09] Ray Optics and Optical Instruments
Other Solutions
Submit Question Paper
Help us maintain new question papers on Shaalaa.com, so we can continue to help studentsonly jpg, png and pdf files
CBSE previous year question papers Class 12 Physics with solutions 2009 - 2010
Previous year Question paper for CBSE Class 12 Physics-2010 is solved by experts. Solved question papers gives you the chance to check yourself after your mock test.
By referring the question paper Solutions for Physics, you can scale your preparation level and work on your weak areas. It will also help the candidates in developing the time-management skills. Practice makes perfect, and there is no better way to practice than to attempt previous year question paper solutions of CBSE Class 12.
How CBSE Class 12 Question Paper solutions Help Students ?
• Question paper solutions for Physics will helps students to prepare for exam.
• Question paper with answer will boost students confidence in exam time and also give you an idea About the important questions and topics to be prepared for the board exam.
• For finding solution of question papers no need to refer so multiple sources like textbook or guides.
