Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Draw the circuit diagram of an illuminated photodiode in reverse bias. How is photodiode used to measure light intensity?
Solution
The circuit diagram of an illuminated photodiode in reverse bias can be represented as

The greater the intensity of light, the greater is the number of photons falling per second per unit area. Thus, the greater the intensity of light, the greater is the number of electron−hole pairs produced at the junction. The photocurrent is, thus, directly proportional to the intensity of light. This can be used for measuring the intensity of incident light.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
If a small voltage is applied to a p-n junction diode, how will the barrier potential be affected when it is (i) forward biased
Using the necessary circuit diagrams, show how the V-I characteristics of a p-n junction are obtained in
Reverse biasing
How are these characteristics made use of in rectification?
Carbon, silicon and germanium have four valence electrons each. These are characterised by valence and conduction bands separated by energy band gap respectively equal to (Eg)C, (Eg)Si and (Eg)Ge. Which of the following statements is true?
Why is zener diode fabricated by heavily doping both p- and n-sides of the junction?
Draw V − I characteristics of a p-n junction diode. Answer the following questions, giving reasons:
(i) Why is the current under reverse bias almost independent of the applied potential up to a critical voltage?
(ii) Why does the reverse current show a sudden increase at the critical voltage?
Name any semiconductor device which operates under the reverse bias in the breakdown region.
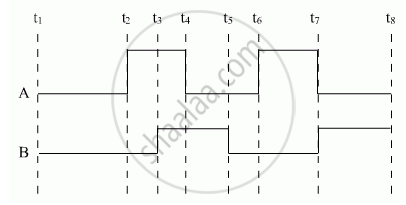
Show the output waveforms (Y) for the following inputs A and B of (i) OR gate (ii) NAND gate ?
The plate resistance of a triode is 8 kΩ and the transconductance is 2.5 millimho. (a) If the plate voltage is increased by 48 V and the grid voltage is kept constant, what will be the increase in the plate current? (b) With plate voltage kept constant at this increased value, by how much should the grid voltage be decreased in order to bring the plate current back to its initial value?
A p-n photodiode is fabricated from a semiconductor with a band gap of 2.5 eV. lt can detect a signal of wavelength ______.
Which one of the following is not the advantage of LED?
Consider the following statements (A) and (B) and identify the correct answer.
- A Zener diode is connected in reverse bias when used as a voltage regulator.
- The potential barrier of the p-n junction lies between 0.1 V to 0.3 V.
