Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Draw the circuit diagram of a full wave rectifier using p-n junction diode.
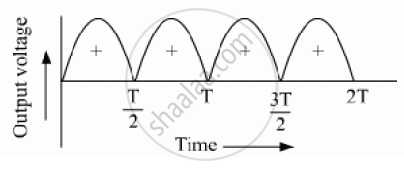
Explain its working and show the output, input waveforms.
Solution


Full wave rectifier:
When the diode rectifies the whole of the AC wave, it is called full wave rectifier.
The figure shows the arrangement for using diode as full wave rectifier. The alternating input signal is fed to the primary P1P2 of a transformer. The output signal appears across the load resistance RL.
During the positive half of the input signal, suppose P1 and P2 are negative and positive respectively. This would mean that S1 and S2 are positive and negative respectively. Therefore, the diode D1 is forward biased and D2 is reverse biased. The flow of current in the load resistance RL is from A to B.
During the negative half of the input signal, S1 and S2 are negative and positive respectively. Therefore, the diode D1 is reverse biased and D2 is forward biased. The flow of current in the load resistance RL is from A to B.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Colour of light emitted by LED depends upon__________________ .
- its forward bias
- its reverse bias
- the band gap of the material of semiconductor
- its size
How is a Zener diode fabricated?
If a small voltage is applied to a p-n junction diode, how will the barrier potential be affected when it is (i) forward biased
Write briefly the important processes that occur during the formation of p−n junction. With the help of necessary diagrams, explain the term 'barrier potential'.
How is a photodiode fabricated?
Draw V − I characteristics of a p-n junction diode. Answer the following questions, giving reasons:
(i) Why is the current under reverse bias almost independent of the applied potential up to a critical voltage?
(ii) Why does the reverse current show a sudden increase at the critical voltage?
Name any semiconductor device which operates under the reverse bias in the breakdown region.
How does a light emitting diode (LED) work? Give two advantages of LED’s over the conventional incandescent lamps.
The plate resistance of a triode is 8 kΩ and the transconductance is 2.5 millimho. (a) If the plate voltage is increased by 48 V and the grid voltage is kept constant, what will be the increase in the plate current? (b) With plate voltage kept constant at this increased value, by how much should the grid voltage be decreased in order to bring the plate current back to its initial value?
Draw the V-I characteristics of an LED. State two advantages of LED lamps over convertional incandescent lamps.
What is a solar cell?
