Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Explain how mutations, natural selection and genetic drift affect Hardy Weinberg equilibrium.
Solution
Natural selection occurs when one allele (or combination of alleles of differences) makes an organism more or less fit to survive and reproduce in a given environment. If an allele reduces fitness, its frequencies tend to drop from one generation to the next.
The evolutionary path of a given gene (i.e) how its allele’s change in frequency in the population across generation, may result from several evolutionary mechanisms acting at once. For example, one gene’s allele frequencies might be modified by both gene flow and genetic drift, for another gene, mutation may produce a new allele, that is favoured by natural selection.
Genetic drift / Sewall Wright Effect is a mechanism of evolution in which allele frequencies of a population change over generation due to chance (sampling error). Genetic drift occurs in all population sizes, but its effects are strong in a small population. It may result in a loss of some alleles (including beneficial ones) and fixation of other alleles. Genetic drift can have major effects, when the population is reduced in size by natural disaster due to bottle neck effect or when a small group of population splits from the main population to form a new colony due to founder’s effect.
Although mutation is the original source of all genetic variation, mutation rate for most organisms is low. Hence new mutations on allele frequencies from one generation to the next is usually not large.
RELATED QUESTIONS
What does the following equation represent? Explain.
p2 + 2pq + q2 = 1
Give the graphical representation of Hardy· Weinberg's principle in the form of Punnet Square.
p2 + 2pq + q2 = 1. Explain this algebraic equation on the basis of Hardy Weinberg's principle.
Differentiate between Directional natural selection and Disruptive natural selection.
How does the Hardy-Wienberg equation explain genetic equilibrium?
Very short answer question.
State the Hardy – Weinberg equilibrium.
In a population, Hardy Weinberg equilibrium is disturbed by following factors EXCEPT ______.
In the Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium equation, the homozygous mutant is represented as ______.
The factor that leads to the Founder effect in a population is ______
Which type of selection explains industrial melanism observed in moth, Biston bitularia ______.
Gene flow occurs through generations. and can occur across language barriers in humans. If we have a technique of measuring specific allele frequencies in different population of the world, can we not predict human migratory patterns in pre-history and history? Do you agree or disagree? Provide explanation to your answer.
Enumerate three most characteristic criteria for designating a Mendelian population.
"Migration may enhance or blurr the effects of selection". Comment.
How is Hardy-Weinberg's expression “(p2 + 2pq + q2) = 1” derived?
The graphs below show three types of natural selection. The shaded areas marked with arrows show the individuals in the population who are not selected. The dotted vertical lines show the statistical means.
 |
 |
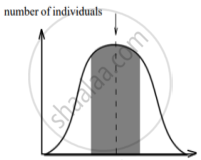 |
| character Graph A |
character Graph B |
character Graph C |
- What names are given to the types of selection shown in graphs A, B and C?
- After the selection has operated for several generations in the above populations indicated as, Graph A, B and C, graphically illustrate the probable results.
State Hardy Weinberg's principle.
A population of 200 fruit flies is in Hardy Weinberg equilibrium. The frequency of the allele (a) 0.4. Calculate the following:
The number of homozygous recessive fruit flies.
The black colour on the beak of finches dominates over the yellow colour. There are 210 individuals with the genotype DD, 245 individuals with the genotype Dd and 45 individuals with the genotype dd. Deduce the frequency of individuals with dominant, heterozygous, and recessive traits.
