Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Show that the diagonals of the parallelogram whose sides are lx + my + n = 0, lx + my + n' = 0, mx + ly + n = 0 and mx + ly + n' = 0 include an angle π/2.
Solution
The given lines are
lx + my + n = 0 ... (1)
mx + ly + n' = 0 ... (2)
lx + my + n' = 0 ... (3)
mx + ly + n = 0 ... (4)
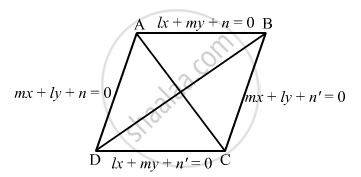
Solving (1) and (2), we get,
\[B \equiv \left( \frac{m n^{\prime}- ln}{l^2 - m^2},\frac{mn - ln^{\prime}}{l^2 - m^2} \right) \]
Solving (2) and (3), we get,
\[C \equiv \left( - \frac{n^{\prime}}{m + l}, - \frac{n^{\prime}}{m + l} \right)\]
Solving (3) and (4), we get,
\[D \equiv \left( \frac{mn - l n^{\prime}}{l^2 - m^2}, \frac{m n^{\prime} - ln}{l^2 - m^2} \right)\]
Solving (1) and (4), we get,
\[A \equiv \left( - \frac{n}{m + l}, - \frac{n}{m + l} \right)\]
Let \[m_1\text { and } m_2 \] be the slope of AC and BD.
\[m_1 = \frac{- \frac{n^{\prime}}{m + l} + \frac{n}{m + l}}{- \frac{n^{\prime}}{m + l} + \frac{n}{m + l}} = 1\]
\[\text { and }m_2 = \frac{\frac{mn' - ln}{l^2 - m^2} - \frac{mn - ln'}{l^2 - m^2}}{\frac{mn - ln'}{l^2 - m^2} - \frac{mn' - ln}{l^2 - m^2}}\]
\[ = \frac{mn' - ln - mn + \ln'}{mn - ln' - mn' + ln}\]
\[ = - 1\]
\[\therefore m_1 m_2 = - 1\]
Hence, diagonals of the parallelogram intersect at an angle \[\frac{\pi}{2}\].
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Find the equation of the line which satisfy the given condition:
Write the equations for the x and y-axes.
Find the equation of the line which satisfy the given condition:
Passing through the point (–4, 3) with slope `1/2`.
Find the equation of the line which satisfy the given condition:
Passing though `(2, 2sqrt3)` and is inclined with the x-axis at an angle of 75°.
Find the equation of the line which satisfy the given condition:
Passing through the points (–1, 1) and (2, –4).
Find the equation of the line which is at a perpendicular distance of 5 units from the origin and the angle made by the perpendicular with the positive x-axis is 30°
Find the equation of the line which satisfy the given condition:
The vertices of ΔPQR are P (2, 1), Q (–2, 3) and R (4, 5). Find equation of the median through the vertex R.
The vertices of ΔPQR are P (2, 1), Q (–2, 3) and R (4, 5). Find equation of the median through the vertex R.
Find the equation of the line passing through (–3, 5) and perpendicular to the line through the points (2, 5) and (–3, 6).
A line perpendicular to the line segment joining the points (1, 0) and (2, 3) divides it in the ratio 1:n. Find the equation of the line.
Find equation of the line through the point (0, 2) making an angle `(2pi)/3` with the positive x-axis. Also, find the equation of line parallel to it and crossing the y-axis at a distance of 2 units below the origin.
The length L (in centimetre) of a copper rod is a linear function of its Celsius temperature C. In an experiment, if L = 124.942 when C = 20 and L = 125.134 when C = 110, express L in terms of C
The owner of a milk store finds that, he can sell 980 litres of milk each week at Rs 14/litre and 1220 litres of milk each week at Rs 16/litre. Assuming a linear relationship between selling price and demand, how many litres could he sell weekly at Rs 17/litre?
Point R (h, k) divides a line segment between the axes in the ratio 1:2. Find equation of the line.
By using the concept of equation of a line, prove that the three points (3, 0), (–2, –2) and (8, 2) are collinear.
Find the values of q and p, if the equation x cos q + y sinq = p is the normal form of the line `sqrt3 x` + y + 2 = 0.
Find the area of the triangle formed by the lines y – x = 0, x + y = 0 and x – k = 0.
Find the image of the point (3, 8) with respect to the line x + 3y = 7 assuming the line to be a plane mirror.
If the lines y = 3x + 1 and 2y = x + 3 are equally inclined to the line y = mx + 4, find the value of m.
Classify the following pair of line as coincident, parallel or intersecting:
2x + y − 1 = 0 and 3x + 2y + 5 = 0
Classify the following pair of line as coincident, parallel or intersecting:
x − y = 0 and 3x − 3y + 5 = 0]
Classify the following pair of line as coincident, parallel or intersecting:
3x + 2y − 4 = 0 and 6x + 4y − 8 = 0.
Prove that the lines \[\sqrt{3}x + y = 0, \sqrt{3}y + x = 0, \sqrt{3}x + y = 1 \text { and } \sqrt{3}y + x = 1\] form a rhombus.
Find the equation to the straight line parallel to 3x − 4y + 6 = 0 and passing through the middle point of the join of points (2, 3) and (4, −1).
Prove that the lines 2x − 3y + 1 = 0, x + y = 3, 2x − 3y = 2 and x + y = 4 form a parallelogram.
Find the equation of the line mid-way between the parallel lines 9x + 6y − 7 = 0 and 3x + 2y + 6 = 0.
Prove that the area of the parallelogram formed by the lines 3x − 4y + a = 0, 3x − 4y + 3a = 0, 4x − 3y− a = 0 and 4x − 3y − 2a = 0 is \[\frac{2}{7} a^2\] sq. units..
Write an equation representing a pair of lines through the point (a, b) and parallel to the coordinate axes.
Three vertices of a parallelogram taken in order are (−1, −6), (2, −5) and (7, 2). The fourth vertex is
