Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
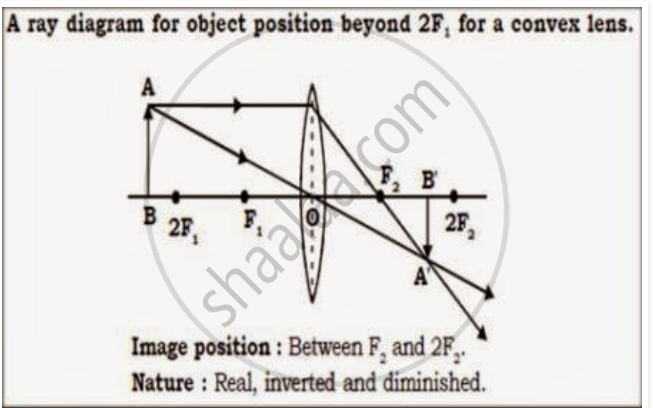
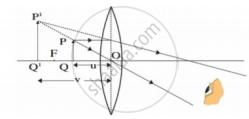
If an object is placed in front of a convex lens beyond 2F1, then what will be the position, relative size, and nature of an image which is formed? Explain with a ray diagram.
Solution
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
An object 5 cm in length is held 25 cm away from a converging lens of focal length 10 cm. Draw the ray diagram and find the position, size and the nature of the image formed.
A beam of light travelling in air is incident of water. Draw a ray-diagram indicating the change in its path in water.
A ray of light travelling in air is incident on a parallel-sided glass slab (or rectangular glass slab). Draw a ray-diagram indicating the change in its path in glass.
Draw a labelled ray diagram to show how a ray of light is refracted when it passes:
from an optically denser medium into air.
Where should an object be placed in front of a convex lens so as to obtain its virtual, erect and magnified image?
Fill in the following blank with suitable word:
Parallel rays of light are refracted by a convex lens to a point called the ........
Distinguish between a convex lens and concave lens. Which of the two is a converging lens : convex lens of concave lens?
Describe with the help of a ray-diagram, the size, nature and position of the image formed by a convex lens when an object is placed beyond 2f in front of the lens.
Describe with the help of a ray diagram the nature, size and position of the image formed when an object is placed at infinity (considerable distance) in front of a convex lens. State three characteristics of the image so formed.
Describe the nature of image formed when an object is placed at a distance of 30 cm from a convex lens of focal length 15 cm.
Find the position and nature of the image of an object 5 cm high and 10 cm in front of a convex lens of focal length 6 cm.
A convex lens produces an inverted image magnified three times of an object placed at a distance of 15 cm from it. Calculate focal length of the lens.
An object 2 cm tall is placed on the axis of a convex lens of focal length 5 cm at a distance of 10 m from the optical centre of the lens. Find the nature, position and size of the image formed. Which case of image formation by convex lenses is illustrated by this example?
Find the nature, position and magnification of the images formed by a convex lens of focal length 0.20 m if the object is placed at a distance of:
0.25 m
A student did an experiment with a convex lens. He put an object at different distances 25 cm, 30 cm, 40 cm, 60 cm and 120 cm from the lens. In each case he measured the distance of the image from the lens. His results were 100 cm, 24 cm, 60 cm, 30 cm and 40 cm, respectively. Unfortunately his results are written in wrong order.
What is the focal length of this lens?
Define the term principal axis of a lens.
A converging lens forms the image of an object placed in front of it, beyond 2F2 of the lens. Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of the image.
The given below figure shows an object OA and its image IB formed by a lens
. 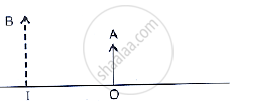
draw suitable rays to locate the lens and its focus.
A lens forms an upright and magnified image of an object State whether the image is real or virtual
In the following cases, where must an object be placed in front of a convex lens so that the image formed is at infinity?
In the following cases, where must an object be placed in front of a convex lens so that the image formed is of the same size as the object?
In the following cases, where must an object be placed in front of a convex lens so that the image formed is inverted and enlarged?
Complete the following table:
| Type of lens | Position of object | Nature of image | Size of image |
| Convex | Between optical centre and focus | ||
| Convex | At focus | ||
| Concave | At infinity | ||
| Concave | At any distance |
State two applications of a convex lens.
If you are to determine to focal length of a convex lens, you should have
(A) a convex lens and a screen
(B) a convex lens and a lens holder
(C) a lens holder, a screen holder and a scale
(D) a convex lens, a screen, holder for them and a scale
For which position of the object does a convex lens form a virtual and erect image? Explain with the help of a ray diagram.
The image obtained while finding the focal length of convex lens is ....................
Where must a point source of light be placed in front of a convex lens so as to obtain a parallel beam of light?
The focal length of a lens is positive. In this case, state the kind of lens.
State the position of object, position of image, nature of image when: Convex lens is used as objective lens of astronomical telescope.
Which lens can produce a real and inverted image of an object?
In the figure given below L is a convex lens, M is a plane mirror and S is a point source of light. Rays of light from the source S return to their point of origin. Complete the ray diagram to show this. What is the point S called?
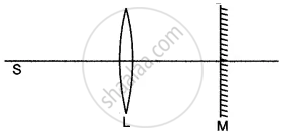
Diagram shows an object AB placed on the principal axis B of a convex lens placed in air. F1 and F2 are the two foci of the lens.
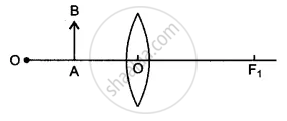
(i) Copy the diagram:
Draw a ray of light starting from B and passing through O. Show the same ray after refraction by the lens. Draw another ray from B which passes through F2 after refraction by the lens. Locate the final image
(ii) Is the image real or virtual?
 : Object near the lens : : ______ :
: Object near the lens : : ______ : 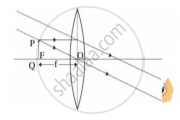
Write scientific reason.
Adults need bifocal lens spectacle.
Convex lens is also known as ______.
Distinguish between Concave lens and Convex Lens.
