Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
If OACB is a parallelogram with \[\overrightarrow{OC} = \vec{a}\text{ and }\overrightarrow{AB} = \vec{b} ,\] then \[\overrightarrow{OA} =\]
Options
- \[\left( \vec{a} + \vec{b} \right)\]
- \[\left( \vec{a} - \vec{b} \right)\]
- \[\frac{1}{2}\left( \vec{b} - \vec{a} \right)\]
- \[\frac{1}{2}\left( \vec{a} - \vec{b} \right)\]
Solution
\[\frac{1}{2}\left( \vec{a} - \vec{b} \right)\]
Given a parallelogram OACB such that \[\overrightarrow{OC} = \vec{a} , \overrightarrow{AB} = \vec{b}\].
Then,
\[\overrightarrow{OB} + \overrightarrow{BC} = \vec{OC} \]
\[ \Rightarrow \overrightarrow{OB} = \overrightarrow{OC} - \overrightarrow{BC}\]
\[\Rightarrow \overrightarrow{OB} = \overrightarrow{OC} - \overrightarrow{OA}\] [∵ \[\overrightarrow{BC} = \overrightarrow{OA}\]]
\[\Rightarrow \overrightarrow{OB} = \vec{a} - \overrightarrow{OA} . . . \left( 1 \right)\]
Therefore,
\[ \overrightarrow{OA} + \overrightarrow{AB} = \overrightarrow{OB} \]
\[ \Rightarrow \overrightarrow{OA} + \vec{b} = \vec{a} - \overrightarrow{OA} \left[ \text { Using } \left( 1 \right) \right]\]
\[ \Rightarrow 2 \overrightarrow{OA} = \vec{a} - \vec{b} \]
\[ \Rightarrow \overrightarrow{OA} = \frac{1}{2} \left( \vec{a} - \vec{b} \right)\]
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
If \[\vec{a}\], \[\vec{b}\], \[\vec{c}\] are the position vectors of the vertices of an equilateral triangle whose orthocentre is at the origin, then write the value of \[\vec{a} + \vec{b} + \vec{c} .\]
Write a unit vector making equal acute angles with the coordinates axes.
Write a unit vector in the direction of \[\overrightarrow{b} = 2 \hat{i} + \hat{j} + 2 \hat{k}\].
Let G be the centroid of ∆ ABC. If \[\overrightarrow{AB} = \vec{a,} \overrightarrow{AC} = \vec{b,}\] then the bisector \[\overrightarrow{AG} ,\] in terms of \[\vec{a}\text{ and }\vec{b}\] is
If ABCDEF is a regular hexagon, then \[\overrightarrow{AD} + \overrightarrow{EB} + \overrightarrow{FC}\] equals
ABCD is a parallelogram with AC and BD as diagonals.
Then, \[\overrightarrow{AC} - \overrightarrow{BD} =\]
Find the components along the coordinate axes of the position vector of the following point :
Q(–5, 1)
Show that the four points having position vectors
\[6 \hat { i} - 7 \hat { j} , 16 \hat {i} - 19 \hat {j}- 4 \hat {k} , 3 \hat {j} - 6 \hat {k} , 2 \hat {i} + 5 \hat {j} + 10 \hat {k}\] are not coplanar.
Find the value of λ for which the four points with position vectors `6hat"i" - 7hat"j", 16hat"i" - 19hat"j" - 4hat"k" , lambdahat"j" - 6hat"k" "and" 2hat"i" - 5hat"j" + 10hat"k"` are coplanar.
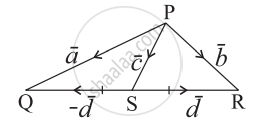
In the given figure express `bar"c"` and `bar"d"` in terms of `bar"a"` and `bar"b"`.
If the sum of two unit vectors is itself a unit vector, then the magnitude of their difference is ______.
Select the correct option from the given alternatives:
If `bar"a" "and" bar"b"` are unit vectors, then what is the angle between `bar"a"` and `bar"b"` for `sqrt3bar"a" - bar"b"` to be a unit vector?
Find the lengths of the sides of the triangle and also determine the type of a triangle:
A(2, -1, 0), B(4, 1, 1), C(4, -5, 4)
Two sides of a parallelogram are `3hat"i" + 4hat"j" - 5hat"k"` and `-2hat"j" + 7hat"k"`. Find the unit vectors parallel to the diagonals.
If P is orthocentre, Q is the circumcentre and G is the centroid of a triangle ABC, then prove that `bar"QP" = 3bar"QG"`.
Dot product of a vector with vectors `3hat"i" - 5hat"k", 2hat"i" + 7hat"j" and hat"i" + hat"j" + hat"k"` are respectively -1, 6 and 5. Find the vector.
Find two unit vectors each of which makes equal angles with bar"u", bar"v" and bar"w" where bar"u" = 2hat"i" + hat"j" - 2hat"k", bar"v" = hat"i" + 2hat"j" - 2hat"k", bar"w" = 2hat"i" - 2hat"j" + hat"k".
State whether the expression is meaningful. If not, explain why? If so, state whether it is a vector or a scalar:
`(bar"a".bar"b") xx (bar"c".bar"d")`
State whether the expression is meaningful. If not, explain why? If so, state whether it is a vector or a scalar:
`(bar"a" xx bar"b").(bar"c"xxbar"d")`
State whether the expression is meaningful. If not, explain why? If so, state whether it is a vector or a scalar:
`(bar"a".bar"b").bar"c"`
For any vectors `bar"a", bar"b", bar"c"` show that `(bar"a" + bar"b" + bar"c") xx bar"c" + (bar"a" + bar"b" + bar"c") xx bar"b" + (bar"b" - bar"c") xx bar"a" = 2bar"a" xx bar"c"`
For any non-zero vectors a and b, [b a × b a] = ?
If the vectors `xhat"i" - 3hat"j" + 7hat"k" and hat"i" + "y"hat"j" - "z"hat"k"` are collinear then the value of `"xy"^2/"z"` is equal.
The vector with initial point P (2, –3, 5) and terminal point Q(3, –4, 7) is ______.
Find a unit vector in the direction of `vec"PQ"`, where P and Q have co-ordinates (5, 0, 8) and (3, 3, 2), respectively
The values of k for which `|"k"vec"a"| < |vec"a"|` and `"k"vec"a" + 1/2 vec"a"` is parallel to `vec"a"` holds true are ______.
If `veca ≠ vec(0), veca.vecb = veca.vecc, veca xx vecb = veca xx vecc`, then show that `vecb = vecc`.
Let `veca, vecb` and `vecc` be three unit vectors such that `veca xx (vecb xx vecc) = sqrt(3)/2 (vecb + vecc)`. If `vecb` is not parallel to `vecc`, then the angle between `veca` and `vecc` is
The unit vector perpendicular to the vectors `6hati + 2hatj + 3hatk` and `3hati - 6hatj - 2hatk` is
Which of the following measures as vector?
Find `|veca xx vecb|`, if `veca = hati - 7hatj + 7hatk` and `vecb = 3hati - 2hatj + 2hatk`
In the triangle PQR, `bar(PQ) = 2bara` and `bar(QR)=2barb`. The mid-point of PR is M. Find following vectors in terms of `bar a and bar b `.
- `bar("PR")`
- `bar("PM")`
- `bar("QM")`
In the triangle PQR, `bar(PQ)` = `2bara` and `bar(QR)` = `2barb`. The mid-point of PR is M. Find following vectors in terms of `bara` and `barb`.
(i) `bar(PR)` (ii) `bar(PM)` (iii) `bar(QM)`
In the triangle PQR, `bb(bar(PQ) = 2 bara)` and `bb(bar(QR) = 2 barb)`. The mid-point of PR is M. Find the following vectors in terms of `bb(bara and barb)`.
- `bar(PR)`
- `bar(PM)`
- `bar(QM)`
Check whether the vectors `2 hati+2 hatj+3 hatk,-3 hati+3 hatj+2 hatk and 3 hati +4 hatk` form a triangle or not.
Check whether the vectors `2hati + 2hatj + 3hatk, -3hati + 3hatj + 2hatk and 3hati + 4hatk` form a triangle or not.
Check whether the vectors `2hati + 2hatj +3hatk, - 3hati + 3hatj + 2hatk and 3hati + 4hatk` form a triangle or not.
