Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
In ΔABC, ∠B = 90°. If AB = 12units and BC = 5units, find: cot C
Solution
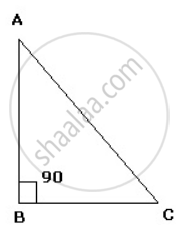
In ΔABC,
AC2 = AB2 + BC2
⇒ AC = `sqrt("AB"^2 + "BC"^2)`
⇒ AC = `sqrt(12^2 + 5^2)`
= `sqrt(144 + 25)`
= 13
AB = 12units
BC = 5units
AC = 13units
cot C
= `"Base"/"Perpendicular"`
= `"BC"/"AB"`
= `(5)/(12)`.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
If ∠A and ∠P are acute angles such that tan A = tan P, then show that ∠A = ∠P.
If A = B = 60°, verify that cos (A − B) = cos A cos B + sin A sin B
In right angled triangle ΔABC at B, ∠A = ∠C. Find the values of sin A sin B + cos A cos B
If A = 300 , verify that:
(ii) cos 2A = `(1- tan^2A)/(1+tan^2A)`
If A = 600 and B = 300, verify that:
(iii) tan (A-B) = `(tan A-tanB)/(1+tan A tan B)`
Using the formula, sin A = `sqrt((1-cos 2A)/2) ` find the value of sin 300, it being given that cos 600 = `1/2`
In the adjoining figure, ΔABC is right-angled at B and ∠A = 450. If AC = 3`sqrt(2)`cm, find (i) BC, (ii) AB.
In the given figure, triangle ABC is right-angled at B. D is the foot of the perpendicular from B to AC. Given that BC = 3 cm and AB = 4 cm.
find :
- tan ∠DBC
- sin ∠DBA

If sin A = `(7)/(25)`, find the value of : cot2A - cosec2A
From the given figure, find the values of sec B