Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
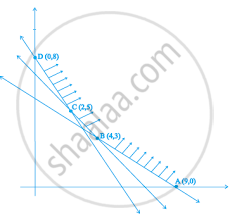
In figure, the feasible region (shaded) for a LPP is shown. Determine the maximum and minimum value of Z = x + 2y.
Solution
Here, corner points are given as follows:
`"R"(7/2, 3/4)`
`"Q"(3/2, 15/4)`
`"P"(3/13, 24/13)`
And `"S"(18/7, 2/7)`
Now, evaluating the value of Z for the feasible region RQPS.
| Corner points | Value of Z = x + 2y | |
| `"R"(7/2, 3/4)` | Z = `7/2 + 2(3/4) = 5` | ← Maximum |
| `"Q"(3/2, 15/4)` | Z = `3/2 + 2(15/4) = 9` | |
| `"P"(3/13, 24/13)` | Z = `3/13 + 2(24/13) = 51/13` | |
| `"S"(18/7, 2/7)` | Z = `18/7 + 2(2/7) = 22/7` | ← Minimum |
Hence, the maximum value of Z is 9 at `(3/2, 15/4)` and the minimum value of Z is `22/7` at `(18/7, 2/7)`
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Solve the following Linear Programming Problems graphically:
Minimise Z = 3x + 5y
such that x + 3y ≥ 3, x + y ≥ 2, x, y ≥ 0.
Show that the minimum of Z occurs at more than two points.
Minimise and Maximise Z = 5x + 10 y
subject to x + 2y ≤ 120, x + y ≥ 60, x – 2y ≥ 0, x, y ≥ 0.
Show that the minimum of Z occurs at more than two points.
Maximise Z = x + y, subject to x – y ≤ –1, –x + y ≤ 0, x, y ≥ 0.
A dietician wishes to mix together two kinds of food X and Y in such a way that the mixture contains at least 10 units of vitamin A, 12 units of vitamin B and 8 units of vitamin C. The vitamin content of one kg food is given below:
| Food | Vitamin A | Vitamin B | Vitamin C |
| X | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| Y | 2 | 2 | 1 |
One kg of food X costs Rs 16 and one kg of food Y costs Rs 20. Find the least cost of the mixture which will produce the required diet?
A manufacturer makes two types of toys A and B. Three machines are needed for this purpose and the time (in minutes) required for each toy on the machines is given below:
| Type of toy | Machines | ||
| I | II | III | |
| A | 12 | 18 | 6 |
| B | 6 | 0 | 9 |
Each machine is available for a maximum of 6 hours per day. If the profit on each toy of type A is Rs 7.50 and that on each toy of type B is Rs 5, show that 15 toys of type A and 30 of type B should be manufactured in a day to get maximum profit.
To maintain his health a person must fulfil certain minimum daily requirements for several kinds of nutrients. Assuming that there are only three kinds of nutrients-calcium, protein and calories and the person's diet consists of only two food items, I and II, whose price and nutrient contents are shown in the table below:
| Food I (per lb) |
Food II (per lb) |
Minimum daily requirement for the nutrient |
||||
| Calcium | 10 | 5 | 20 | |||
| Protein | 5 | 4 | 20 | |||
| Calories | 2 | 6 | 13 | |||
| Price (Rs) | 60 | 100 |
What combination of two food items will satisfy the daily requirement and entail the least cost? Formulate this as a LPP.
Maximise Z = 3x + 4y, subject to the constraints: x + y ≤ 1, x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0
Minimise Z = 13x – 15y subject to the constraints: x + y ≤ 7, 2x – 3y + 6 ≥ 0, x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0
Feasible region (shaded) for a LPP is shown in Figure. Maximise Z = 5x + 7y.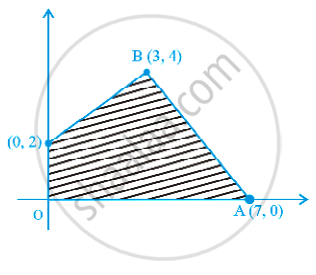
Refer to Exercise 7 above. Find the maximum value of Z.
Refer to quastion 12. What will be the minimum cost?
Refer to question 14. How many sweaters of each type should the company make in a day to get a maximum profit? What is the maximum profit.
The corner points of the feasible region determined by the system of linear constraints are (0, 0), (0, 40), (20, 40), (60, 20), (60, 0). The objective function is Z = 4x + 3y ______.
Compare the quantity in Column A and Column B
| Column A | Column B |
| Maximum of Z | 325 |
The feasible solution for a LPP is shown in Figure. Let Z = 3x – 4y be the objective function. Minimum of Z occurs at ______.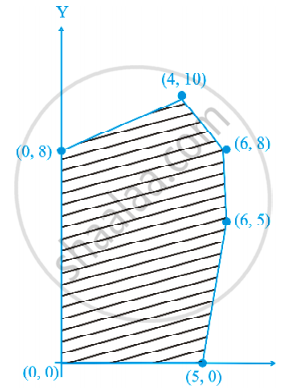
Refer to Question 27. Maximum of Z occurs at ______.
Corner points of the feasible region for an LPP are (0, 2), (3, 0), (6, 0), (6, 8) and (0, 5). Let F = 4x + 6y be the objective function. The Minimum value of F occurs at ______.
Refer to Question 32, Maximum of F – Minimum of F = ______.
In a LPP, the linear inequalities or restrictions on the variables are called ____________.
In a LPP if the objective function Z = ax + by has the same maximum value on two corner points of the feasible region, then every point on the line segment joining these two points give the same ______ value.
If the feasible region for a LPP is unbounded, maximum or minimum of the objective function Z = ax + by may or may not exist.
A linear programming problem is as follows:
Minimize Z = 30x + 50y
Subject to the constraints: 3x + 5y ≥ 15, 2x + 3y ≤ 18, x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0
In the feasible region, the minimum value of Z occurs at:
For an objective function Z = ax + by, where a, b > 0; the corner points of the feasible region determined by a set of constraints (linear inequalities) are (0, 20), (10, 10), (30, 30) and (0, 40). The condition on a and b such that the maximum Z occurs at both the points (30, 30) and (0, 40) is:
If two corner points of the feasible region are both optimal solutions of the same type, i.e., both produce the same maximum or minimum.
Maximize Z = 3x + 5y, subject to x + 4y ≤ 24, 3x + y ≤ 21, x + y ≤ 9, x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0.
Maximize Z = 4x + 6y, subject to 3x + 2y ≤ 12, x + y ≥ 4, x, y ≥ 0.
Maximize Z = 7x + 11y, subject to 3x + 5y ≤ 26, 5x + 3y ≤ 30, x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0.
The feasible region for an LPP is shown shaded in the following figure. Minimum of Z = 4x + 3y occurs at the point.