Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
In the given figure, AB and DE are perpendiculars to BC.
Prove that : ΔABC ~ ΔDEC
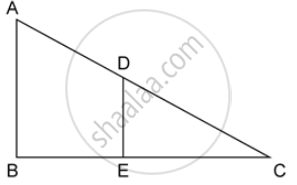
Solution
In ΔABC and ΔDEC,
∠ABC = ∠DEC ...(both are right angles)
∠ACB = ∠DCE ....(common angles)
ΔABC ∼ ΔDEC ...(AA criterion for similarity)
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
In the following figure, XY is parallel to BC, AX = 9 cm, XB = 4.5 cm and BC = 18 cm.
Find : XY
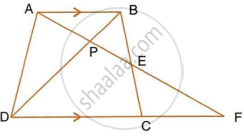
In the following figure, ABCD to a trapezium with AB ‖ DC. If AB = 9 cm, DC = 18 cm, CF = 13.5 cm, AP = 6 cm and BE = 15 cm, Calculate: PE
In the given figure, AB and DE are perpendiculars to BC.
Find the ratio of the area of a ΔABC : area of ΔDEC.

ABC is a right angled triangle with ∠ABC = 90°. D is any point on AB and DE is perpendicular to AC. Prove that :

ΔADE ~ ΔACB.
ABC is a right angled triangle with ∠ABC = 90°. D is any point on AB and DE is perpendicular to AC. Prove that :
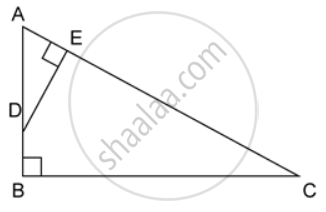
If AC = 13 cm, BC = 5 cm and AE = 4 cm. Find DE and AD.
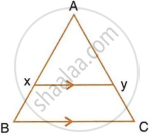
In ΔABC, and E are the mid-points of AB and AC respectively. Find the ratio of the areas of ΔADE and ΔABC.
On a map drawn to a scale of 1 : 2,50,000; a triangular plot of land has the following measurements : AB = 3 cm, BC = 4 cm and angle ABC = 90°.
Calculate:
- the actual lengths of AB and BC in km.
- the area of the plot in sq. km.
In the given figure ABC is a triangle with ∠EDB = ∠ACB.
(i) Prove that ΔABC ∼ ΔEBD.
(ii) If BE = 6 cm, EC = 4 cm, BD = 5 cm and area of ΔBED = 9 cm2. Calculate the length of AB and area of ΔABC.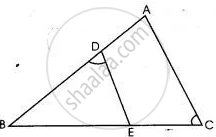
In the figure below, PB and QA are perpendiculars to the line segment AB. If PO = 6 cm, QO = 9 cm and the area of ΔPOB = 120 cm2, find the area of ΔQOA.
In the given figure ΔABC and ΔAMP are right angled at B and M respectively.
Given AC = 10 cm, AP = 15 cm and PM = 12 cm.
(i) Prove ΔABC ∼ Δ AMP.
(ii) Find AB and BC.
