Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Liquid ammonia is used in ice factory for making ice from water. If water at 20°C is to be converted into 2 kg ice at 0°C, how many grams of ammonia are to be evaporated? (Given: The latent heat of vaporization of ammonia = 341 cal/g)
Solution
Given: 1) Change in temperature of water (ΔT) = 20° C
2) mass of ice (m) = 2 kg = 2000 g/2 × 103 g
3) `("L"_"vap")_"ammonia"` = 341 cal/g
4) Specific heat of wate (Cw) = 1 cal/g° C
5) `("L"_"melt")_"ice"` = 80 cal/g
Find: Mass of ammonia (M)
1) Amount of heat released in converting water at 20° C to water at 0°C (Q1)
Q1 = m × c × ΔT
= 2 × 103 × 1 × 20
Q1 = 40 × 103 cal
2) Amount of heat released in converting water at 0° C into ice at 0° C (Q2)
Q2 = mw × Lmelt
= 2 × 103 × 80
= 160 × 103 cal
Total heat given out (Q3) = Q1 + Q2
Q3 = (40 + 160)103
Q3 = 200 × 103 cal
According to principle of heat exchange - heat released by water is used by liquid ammonia
Q3 = `"M""L"_(("vap")_("ammonia"))`
200 × 103 = M × 341
M = `(200 xx 10^3)/341`
M = 586.5 g
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
State the effect of an increase of impurities on the melting point of ice.
1 g ice of 0℃ melts to form 1 g water at 0℃. State whether the latent heat is absorbed or given out by ice.
Which has more heat: 1 g ice at 0℃ or 1g water 0℃? Give reason.
Calculate the total amount of heat energy required to convert 100 g of ice at −10℃ completely into water at 100℃. Specific heat capacity of ice = 2.1 J g-1 K-1, specific heat capacity of water = 4.2 J g-1K-1, specific latent heat of ice = 336 J g-1.
Explain the following temperature vs time graph.

What is meant by latent heat? How will the state of matter transform if latent heat is given off?
Define the following terms:
(i) Specific latent heat,
(ii) Specific latent heat of fusion.
A substance changes from its solid state to the liquid state when heat is supplied to it. What name is given to heat absorbed by the substance.
When 1 g of ice at 0 °C melts to form 1 g of water at 0 °C then, is the latent heat absorbed by the ice or given out by it?
Explain the statement; “The specific latent heat of vaporization of wafer is 2260 × 103 J/kg”.
What do you understand by the ‘latent heat of vaporization’ of a substance?
Calculate the total amount of heat required to convert 100g ice at 0°C to steam at 100°C.
(Specific latent heat of fusion of ice = 336 J/g, specific latent heat of vaporization of steam = 2260 J/g, specific heat capacity of water = 4.2 J/g°C).
When ice is converted into water : constant temperature : : before the water evaporates : _______
Write the name.
The phase in which solid substances are converted into liquid.
Specific latent heat L = ______.
Specific latent heat of a substance ______.
The diagram below shows a cooling curve for a substance:
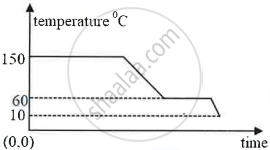
- State the temperatures at which the substance condenses.
- The temperature range in which the substance is in liquid state.
- Why do we prefer ice to ice-cold water for cooling a drink?
