Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A substance changes from its solid state to the liquid state when heat is supplied to it. What name is given to heat absorbed by the substance.
Solution
Latent heat of melting.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
State two characteristics of a good thermion emitter.
Explain the following:
The heat supplied to a substance during it change of state, does not cause any rise in its temperature.
Calculate the total amount of heat energy required to convert 100 g of ice at −10℃ completely into water at 100℃. Specific heat capacity of ice = 2.1 J g-1 K-1, specific heat capacity of water = 4.2 J g-1K-1, specific latent heat of ice = 336 J g-1.
Explain the following temperature vs time graph.

Explain the following temperature Vs. time graph:
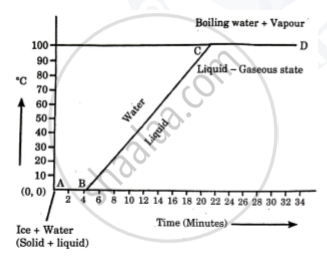
State two advantages of the high specific latent heat capacity of steam, which is about 226 × 104 J/kg?
What observation you will record and how will you determine the specific latent heat of fusion of ice?
Steam at 100°C is passed over 1000 g of ice at 0°C. After some time, 600 g of ice at 0°C is left and 450 g of water at 0°C is formed. Calculate the specific latent heat of vaporization of steam (Given: specific heat capacity of water = 4200 J/kg°C, specific latent heat of fusion of ice = 336,000 J/kg.)
How fog is formed?
Write the name.
Products obtained when sugar is heated.
Write the name.
The phase in which solid substances are converted into liquid.
Define specific latent heat capacity
For the same mass of ice and ice-cold water, why does ice produce more cooling than ice-cold water?
Who introduced the term latent heat?
600 g of copper at 50°C is mixed with lOOOg water at 20°C. Find the final temperature of the mixture. The specific heat capacity of copper is 0.4 Jg-1°C-1 and that of water is 4.2 Jg-1°C-1
