Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Observe the diagram given below and answer the questions:
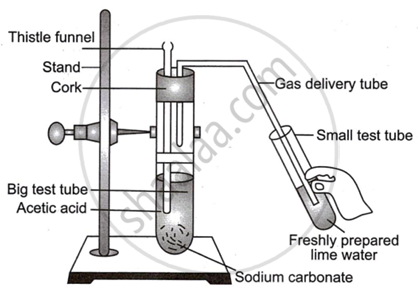
- Name the reactants in this reaction.
- Which gas comes out as effervescence in the bigger test tube?
- What is the colour change in the lime water?
- In the above experiment instead of sodium carbonate which chemical can be used to get same products?
- Write the use of acetic acid.
Solution
- The reactants are acetic acid \[\ce{(CH3COOH)}\] and sodium carbonate \[\ce{(Na2CO3)}\].
- The gas produced is carbon dioxide \[\ce{(CO2)}\].
- When carbon dioxide gas is passed through lime water, it turns lime water milky or cloudy due to the formation of calcium carbonate. Therefore, the colour change in the lime water would be from clear to milky.
- In the above experiment, instead of sodium carbonate, sodium bicarbonate can be used to get the same products.
- Acetic acid is widely used in the culinary arts as a key ingredient in vinegar. It is also used industrially as a chemical reagent for the production of chemical compounds, in the manufacture of plastics, and in the food industry as a preservative and flavouring agent.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Consider the following comments about saponification reactions:
I. Heat is evolved in these reactions.
II. For quick precipitation of soap, sodium chloride is added to the reaction mixtures.
III. Saponification reactions are a special kind of neutralisation reactions.
IV. Soaps are basic salts of long-chain fatty acids.
The correct comments are
(a) I, II and III
(b) II, III and IV
(c) I, II and IV
(d) Only I and IV
What do you observe when you drop a few drops of acetic acid to test tubes containing
(a) phenolphthalein
(b) distilled water
(c) universal indicator
(d) sodium hydrogen carbonate powder
While studying saponification reaction for the preparation of soap, a teacher suggested to a student to add a small quantity of common salt to the reaction mixture. The function of common salt in this reaction is to
(A) reduce the alkalinity of the soap
(B) reduce the acidity of the soap
(C) enhance the cleansing capacity of soap
(D) favour precipitation of soap
Give the common names and IUPAC names of the following compounds of HCOOH.
Give the name and structural formula of one homologue of HCOOH.
Write the formulae of methanoic acid.
Name the gas evolved when ethanoic acid is added to sodium carbonate. How would you prove the presence of this gas?
Name the functional group present in an organic compound which gives brisk effervescence with NaHCO3.
An organic compound A (molecular formula C2H4O2) reacts with Na metal to form a compound B and evolves a gas which burns with a pop sound. Compound A on treatment with an alcohol C in the presence of a little of concentrated sulphuric acid forms a sweet-smelling compound D (molecular formula C3H6O2). Compound D on treatment with NaOH solution gives back B and C. Identify A, B, C and
Acetic acid is a typical acid. Write one equation in case of its reactions with a metal?
Under what conditions does ethane get converted to ethyl alcohol?
Give balanced chemical equations for the following conversion:
Calcium carbide to ethyne
Identify the term or substance based on the descriptions given below:
Ice like crystals formed on cooling an organic acid sufficiently.
Choose the correct alternative and rewrite the following:
Some acetic acid is treated with solid NaHCO3, the resulting solution will be _________________.
Write the characteristics of ethanoic acid.
Mineral acids are stronger acids than carboxylic acids because
- mineral acids are completely ionised
- carboxylic acids are completely ionised
- mineral acids are partially ionised
- carboxylic acids are partially ionised
Ester is formed by the reaction between ______.
Give the balanced chemical equation of the following reaction:
Neutralization of NaOH with ethanoic acid.
Give the balanced chemical equation of the following reaction:
Neutralization of NaOH with ethanoic acid.
