Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Observe the figure and name the ray AB, ray CD, ray GH.

Solution
- Ray AB - Incident ray
- Ray CD - Refracted ray
- Ray GH - Emergent ray
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Choose the correct alternative and rewrite the following sentence.
A ray of light strikes the glass slab at an angle of 50°. What is the angle of incidence?
Draw a ray diagram to show the refraction of light through a glass slab and mark angle of refraction and the lateral shift suffered by the ray of light while passing through the slab.
Why do we get a spectrum of seven colors when white light is dispersed by a prism?
Which colour of light travels fastest in any medium except air?
Why is the ratio of the velocities of light of wavelengths 4000Å and 8000Å in vacuum 1: 1?
How can you bend light away from the normal?
Draw diagrams to show the refraction of light from
- air to glass, and
- glass to air. In each diagram, label the incident ray, refracted ray, the angle of incidence
- and the angle of refraction (r).
For which colour of white light, is the refractive index of a transparent medium the most?
A ray of light strikes the surface of a rectangular glass block such that the angle of incidence in
air is 0°.
In each case, draw diagram to show the path taken by the ray as it passes through the glass block and emerges from it.
In the adjacent diagram, AO is a ray of light incident on a rectangular glass slab.
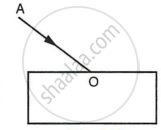
- Complete the path of the ray till it emerges out of the slab.
- In the diagram, mark the angle of incidence (i) and the angle of refraction (r) at the first interface. How is the refractive index of glass related to the angles i and r?
- Mark angles of emergence by the letter e. How are the angles i and e related?
- Which two rays are parallel to each other? Name them.
- Indicate in the diagram the lateral displacement between the emergent ray and the incident ray. State one factor that affects the lateral displacement.
How does the angle of minimum deviation produces by a prism change with increase in :
the wavelength of incident light
How does the speed of light change when it passes from glass to water?
The diagram alongside shows the refraction of a ray of light from air to a liquid.
- Write the values of (i) angle of incidence, (ii) angle of refraction.
- Use Snell’s law to find the refractive index of liquid with respect to air.

Fill in the blanks to complete the following sentence
The refractive index of glass with respect to air is 3/2. The refractive index of air with respect to glass will be ……………….
Trace the path of a ray of light incident at an angle of 45° on a rectangular glass slab. Write the measure of the angle of refraction, the angle of emergence and the lateral displacement suffered by the ray as it passes through the slab.
Four students showed the following traces of the path of a ray of light passing through a rectangular glass slab.
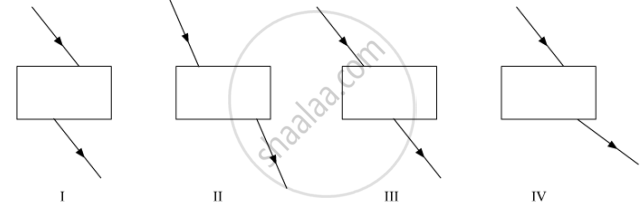
The trace most likely to be correct is that of student
(A) I
(B) II
(C) III
(D) IV
In the fig. name the ray which represents the correct path of light while passing through a glass block.
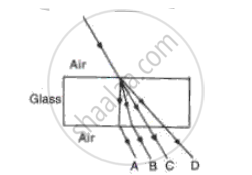
Make the correct for each of the following :
With reference to the fig, the refractive index of the glass block is
A ray of light strikes the surface at a rectangular glass slab such that the angle of incidence is 45o.
In each case, draw diagram to show the path taken by the ray as it passes through the glass slab and emerges from it.
A total reflecting equilateral prism can be used to deviate a ray of light through:
Why is the colour red used as a sign of danger?
During sunset and sunrise, the sun is seen when it is slightly below the horizon. Give reason.
Can the absolute refractive index of a medium be less than one?
Why does the sun appear bigger during sunset or sunrise?
Name two instruments of the total refracting prism in which is used.
In what condition a prism is said to be in the position of minimum deviation? What is the direction of the refracted ray inside the prism in this condition?
What do you understand by the deviation produced by a prism?
Draw ray of light bending towards the normal while passing from air to glass. Label your diagrams.
Trace a ray of light incident at 30° on a surface if travelling from glass to air. What is the angle of refraction in this case? (R.I. for glass = 3/2).
Explain with the help of a diagram of how fish is able to see the objects above it.
Draw a diagram of a prism and label:
(i) the base,
(ii) the refracting surfaces,
(iii) the refracting edge,
(iv) the refracting angle in it.
A ray of light PQ is incident normally on the hypotenuse of a right-angled prism ABC as shown in the diagram given below:
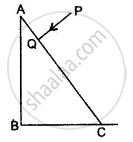
(i) Copy the diagram and complete the path of the ray PQ till it emerges from the prism.
(ii) What is the value of the angle of deviation of the ray?
(iii) Name an instrument where this action of the prism is used.
The velocity of light in diamond is 121000 kms-1. What is its refractive index?
A coin placed at the bottom of a beaker appears to be raised by 4.0 cm. If the refractive index of water is 4/3, find the depth of the water in the beaker.
A ray of light strikes the surface of a rectangular glass slab such that the angle of incidence in air is
- 0°,
- 45°.
In each case, draw a diagram to show the path taken by the ray as it passes through the glass slab and emerges from it.
