Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Out of (CH3)3 C-Br and (CH3)3 C-I, which one is more reactive towards SN1 and why?
Solution
In SN1 reactions, reactivity depends on the stability of carbocation after removing the leaving group form the reactant. Since the carbocation is the same here, so, we will see the tendency of leaving the group. As we can see in the following reactions Br and r are the leaving groups, out of them r is a better leaving group. Hence SN1 reaction will be faster in (CH3)3 C-I (CH3)3 - Br
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{CH3}\phantom{..............}\ce{CH3}\\
\phantom{.}|\phantom{.................}|\phantom{...}\\
\ce{CH3-C-Br->CH3-C^+ + Br^-}\\
\phantom{.}|\phantom{.................}|\phantom{...}\\\ce{CH3}\phantom{..............}\ce{CH3}\\
\end{array}\]
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\phantom{...}\ce{CH3}\phantom{............}\ce{CH3}\\
\phantom{...}|\phantom{...............}|\phantom{...}\\
\ce{CH3-C-I->CH3-C^+ + I^-}\\
\phantom{...}|\phantom{...............}|\phantom{...}\\
\phantom{...}\ce{CH3}\phantom{............}\ce{CH3}\\
\end{array}\]
RELATED QUESTIONS
What happens when \[\ce{CH3 - Br}\] is treated with KCN?
Chlorobenzene is extremely less reactive towards a nucleophilic substitution reaction. Give two reasons for the same.
Write the final product(s) in each of the following reactions:
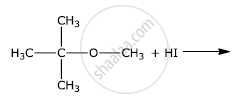
The presence of nitro group (−NO2) at o/p positions increases the reactivity of haloarenes towards nucleophilic substitution reactions.
Give reasons:
The dipole moment of chlorobenzene is lower than that of cyclohexyl chloride.
Assertion: Presence of a nitro group at ortho or para position increases the reactivity of haloarenes towards nucleophilic substitution.
Reason: Nitro group, being an electron-withdrawing group decreases the electron density over the benzene ring.
Which of the following compounds will give racemic mixture on nucleophilic substitution by \[\ce{OH-}\] ion?
(a) \[\begin{array}{cc}
\phantom{}\ce{CH3 - CH - Br}\\
\phantom{}|\\
\phantom{....}\ce{C2H5}\phantom{}
\end{array}\]
(b) \[\begin{array}{cc}
\phantom{..}\ce{Br}\\
\phantom{}|\\
\phantom{}\ce{CH3 - C - CH3}\\
\phantom{}|\\
\phantom{....}\ce{C2H5}\phantom{}
\end{array}\]
(c) \[\begin{array}{cc}
\phantom{....}\ce{CH3 - CH - CH2Br}\\
\phantom{}|\\
\phantom{....}\ce{C2H5}\phantom{}
\end{array}\]
Arrange the following compounds in increasing order of rate of reaction towards nucleophilic substitution.
| (a) | 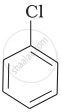 |
| (b) | 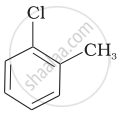 |
| (c) | 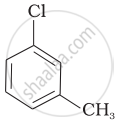 |
\[\ce{C6H12O6 ->[(Zymase)] A ->[NaOH][\Delta] B + CHI3}\]
The number of carbon atoms present in the product B is:
Assertion: Chlorobenzene is resistant to nucleophilic substitution reaction at room temperature.
Reason (R): C–Cl bond gets weaker due, to resonance.
