Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Prove that the diagonals of a kite intersect each other at right angles.
Solution
Consider ABCD is a kite.
Then, AB = AD and BC = DC
In ΔABC and ΔADC,
AB = AD
BC = CD
AC = AC
∴ ΔABC ≅ ΔADC ...(SSS Congruence)
⇒ ∠BCA = ∠DCA ...(C.P.C.T)
⇒ ∠BCO = ∠DCO ...(i)
Now,
In ΔOBC and ΔODC,
BC = CD
∠BCO = ∠DCO ...[From (i)]
OC = OC ...(common)
∴ ΔOBC ≅ ΔODC ...(SAS congruence)
∠COB - ∠COD ...(C. C.T)
But, ∠COB + ∠CID = 180° ...(Linear pair)
⇒ ∠COB + ∠COB = 180°
⇒ 2∠COB = 180°
⇒ ∠COB = 90°
Hence, diagonals f a kite intersect each other at right angles.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
SN and QM are perpendiculars to the diagonal PR of parallelogram PQRS.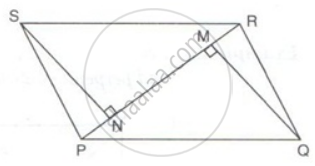
Prove that:
(i) ΔSNR ≅ ΔQMP
(ii) SN = QM
PQRS is a parallelogram. PQ is produced to T so that PQ = QT. Prove that PQ = QT. Prove that ST bisects QR.
ABCD is a quadrilateral P, Q, R and S are the mid-points of AB, BC, CD and AD. Prove that PQRS is a parallelogram.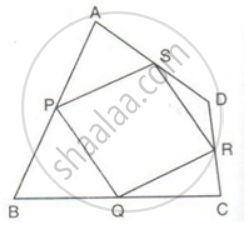
P is a point on side KN of a parallelogram KLMN such that KP : PN is 1 : 2. Q is a point on side LM such that LQ : MQ is 2 : 1. Prove that KQMP is a parallelogram.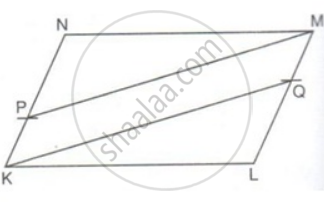
In a parallelogram PQRS, M and N are the midpoints of the opposite sides PQ and RS respectively. Prove that
PMRN is a parallelogram.
ABCD is a trapezium in which side AB is parallel to side DC. P is the mid-point of side AD. IF Q is a point on the Side BC such that the segment PQ is parallel to DC, prove that PQ = `(1)/(2)("AB" + "DC")`.
In the given figure, PQRS is a parallelogram in which PA = AB = Prove that: SAQB is a parallelogram.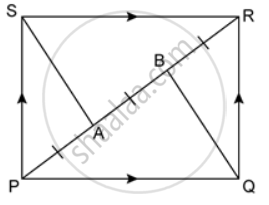
The diagonals AC and BC of a quadrilateral ABCD intersect at O. Prove that if BO = OD, then areas of ΔABC an ΔADC area equal.
In the given figure, PQ ∥ SR ∥ MN, PS ∥ QM and SM ∥ PN. Prove that: ar. (SMNT) = ar. (PQRS).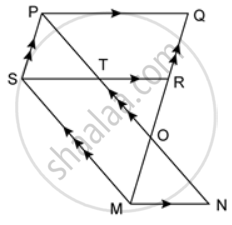
In ΔABC, the mid-points of AB, BC and AC are P, Q and R respectively. Prove that BQRP is a parallelogram and that its area is half of ΔABC.
