Advertisements
Chapters
2: Profit , Loss and Discount
3: Compound Interest
4: Expansions
5: Factorisation
6: Changing the subject of a formula
7: Linear Equations
8: Simultaneous Linear Equations
9: Indices
10: Logarithms
11: Triangles and their congruency
12: Isosceles Triangle
13: Inequalities in Triangles
14: Constructions of Triangles
15: Mid-point and Intercept Theorems
16: Similarity
17: Pythagoras Theorem
18: Rectilinear Figures
▶ 19: Quadrilaterals
20: Constructions of Quadrilaterals
21: Areas Theorems on Parallelograms
22: Statistics
23: Graphical Representation of Statistical Data
24: Perimeter and Area
25: Surface Areas and Volume of Solids
26: Trigonometrical Ratios
27: Trigonometrical Ratios of Standard Angles
28: Coordinate Geometry
![Frank solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 9 ICSE chapter 19 - Quadrilaterals Frank solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 9 ICSE chapter 19 - Quadrilaterals - Shaalaa.com](/images/mathematics-english-class-9-icse_6:c41cc344f5174c64a036c55d113af73f.jpg)
Advertisements
Solutions for Chapter 19: Quadrilaterals
Below listed, you can find solutions for Chapter 19 of CISCE Frank for Mathematics [English] Class 9 ICSE.
Frank solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 9 ICSE 19 Quadrilaterals Exercise 19.1
In the following figures, find the remaining angles of the parallelogram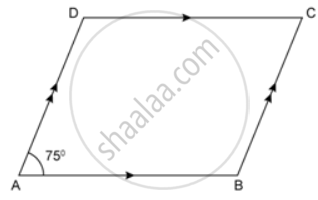
In the following figures, find the remaining angles of the parallelogram
In the following figures, find the remaining angles of the parallelogram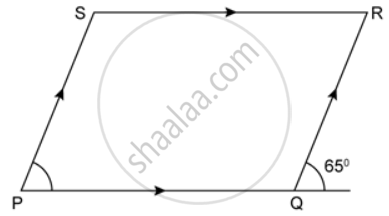
In the following figures, find the remaining angles of the parallelogram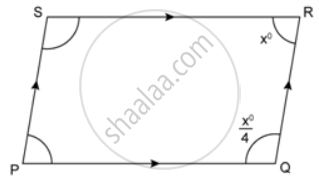
In the following figures, find the remaining angles of the parallelogram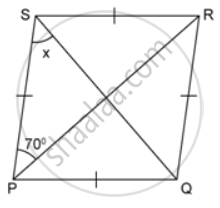
In a parallelogram ABCD ∠C = 98°. Find ∠A and ∠B.
The consecutive angles of a parallelogram are in the ratio 3:6. Calculate the measures of all the angles of the parallelogram.
Find the measures of all the angles of the parallelogram shown in the figure: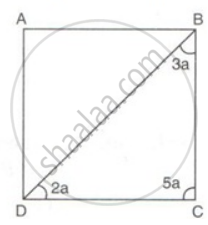
In the given figure, ABCD is a parallelogram, find the values of x and y.
The angles of a triangle formed by 2 adjacent sides and a diagonal of a parallelogram are in the ratio 1 : 5 : 3. Calculate the measures of all the angles of the parallelogram.
PQR is a triangle formed by the adjacent sides PQ and QR and diagonal PR of a parallelogram PQRS. If in ΔPQR, ∠P : ∠Q : ∠R = 3 : 8 : 4, Calculate the measures of all the angles of parallelogram PQRS.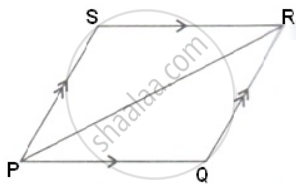
PQRS is a parallelogram. T is the mid-point of PQ and ST bisects ∠PSR.
Prove that: QR = QT
PQRS is a parallelogram. T is the mid-point of PQ and ST bisects ∠PSR.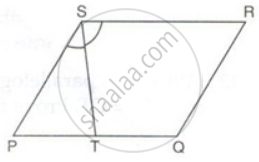
Prove that: RT bisects angle R
PQRS is a parallelogram. T is the mid-point of PQ and ST bisects ∠PSR.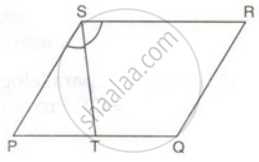
Prove that: ∠RTS = 90°
ABCD is a parallelogram. The bisector of ∠BAD meets DC at P, and AD is half of AB.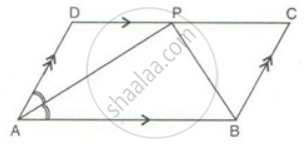
Prove that: BP bisects ∠ABC.
ABCD is a parallelogram. The bisector of ∠BAD meets DC at P, and AD is half of AB.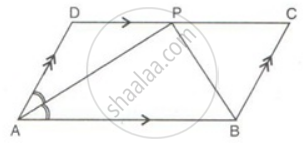
Prove that: ∠APB is a right angle.
ABCD is a parallelogram. P and Q are mid-points of AB and CD. Prove that APCQ is also a parallelogram.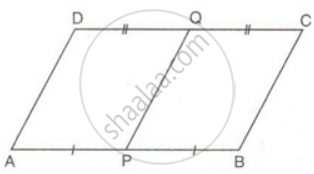
SN and QM are perpendiculars to the diagonal PR of parallelogram PQRS.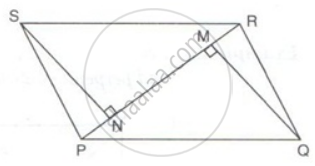
Prove that:
(i) ΔSNR ≅ ΔQMP
(ii) SN = QM
Points M and N are taken on the diagonal AC of a parallelogram ABCD such that AM = CN. Prove that BMDN is a parallelogram.
In the given figure, MP is the bisector of ∠P and RN is the bisector of ∠R of parallelogram PQRS. Prove that PMRN is a parallelogram.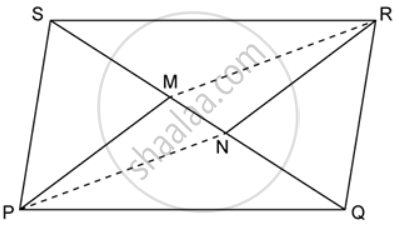
ABCD is a parallelogram. P and T are points on AB and DC respectively and AP = CT. Prove that PT and BD bisect each other.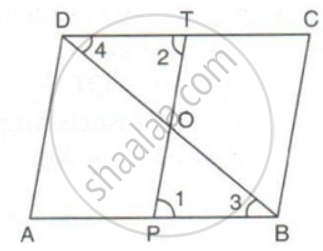
PQRS is a parallelogram. PQ is produced to T so that PQ = QT. Prove that PQ = QT. Prove that ST bisects QR.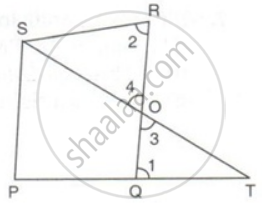
Frank solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 9 ICSE 19 Quadrilaterals Exercise 19.2
PQRS is a square whose diagonals PR and QS intersect at O.M is a point on QR such that OQ = MQ. Find the measures of ∠MOR and ∠QSR.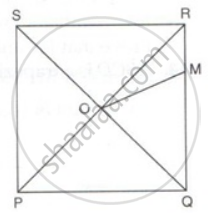
ABCD is a rectangle with ∠ADB = 55°, calculate ∠ABD.
Prove that if the diagonals of a parallelogram are equal then it is a rectangle.
Prove that the quadrilateral formed by joining the mid-points of a square is also a square.
The diagonals PR and QS of a quadrilateral PQRS are perpendicular to each other. A, B, C and D are mid-point of PQ, QR, RS and SP respectively. Prove that ABCD is a rectangle.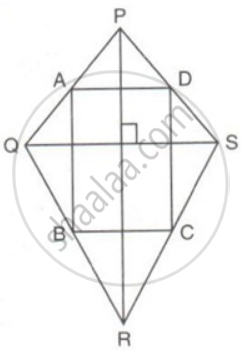
ABCD is a quadrilateral P, Q, R and S are the mid-points of AB, BC, CD and AD. Prove that PQRS is a parallelogram.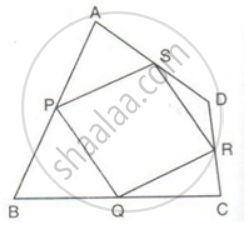
Prove that the quadrilateral formed by joining the mid-points of consecutive sides of a rectangle is a rhombus.
Prove that the quadrilateral formed by joining the mid-points of consecutive sides of a rhombus is a rectangle.
PQRS is a parallelogram. T is the mid-point of RS and M is a point on the diagonal PR such that MR = `(1)/(4)"PR"`. TM is joined and extended to cut QR at N. Prove that QN = RN.
P is a point on side KN of a parallelogram KLMN such that KP : PN is 1 : 2. Q is a point on side LM such that LQ : MQ is 2 : 1. Prove that KQMP is a parallelogram.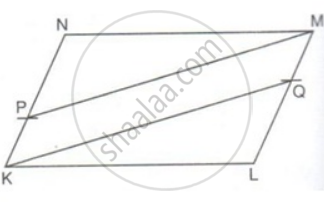
PQRS is a parallelogram. M and N are the mid-points of the adjacent sides QR and RS. O is the mid-point of the diagonal PR. Prove that MONR is a rectangle and MN is half of PR.
Prove that the line segment joining the mid-points of the diagonals of a trapezium is parallel to each of the parallel sides, and is equal to half the difference of these sides.
In a parallelogram PQRS, M and N are the midpoints of the opposite sides PQ and RS respectively. Prove that
RN and RM trisect QS.
In a parallelogram PQRS, M and N are the midpoints of the opposite sides PQ and RS respectively. Prove that
PMRN is a parallelogram.
In a parallelogram PQRS, M and N are the midpoints of the opposite sides PQ and RS respectively. Prove that
MN bisects QS.
ABCD is a trapezium in which side AB is parallel to side DC. P is the mid-point of side AD. IF Q is a point on the Side BC such that the segment PQ is parallel to DC, prove that PQ = `(1)/(2)("AB" + "DC")`.
In the given figure, PQRS is a parallelogram in which PA = AB = Prove that: SA ‖ QB and SA = QB.
In the given figure, PQRS is a parallelogram in which PA = AB = Prove that: SAQB is a parallelogram.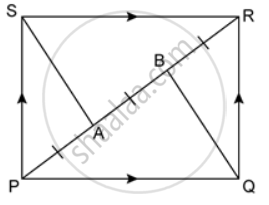
In the given figure, PQRS is a trapezium in which PQ ‖ SR and PS = QR. Prove that: ∠PSR = ∠QRS and ∠SPQ = ∠RQP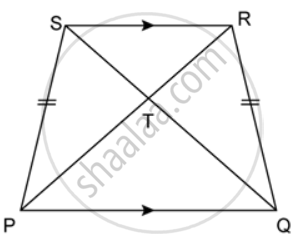
In a parallelogram ABCD, E is the midpoint of AB and DE bisects angle D. Prove that: BC = BE.
In a parallelogram ABCD, E is the midpoint of AB and DE bisects angle D. Prove that:CE is the bisector of angle C and angle DEC is a right angle
Prove that if the diagonals of a quadrilateral bisect each other at right angles then it is a rhombus.
Prove that the diagonals of a kite intersect each other at right angles.
Prove that the diagonals of a square are equal and perpendicular to each other.
Solutions for 19: Quadrilaterals
![Frank solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 9 ICSE chapter 19 - Quadrilaterals Frank solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 9 ICSE chapter 19 - Quadrilaterals - Shaalaa.com](/images/mathematics-english-class-9-icse_6:c41cc344f5174c64a036c55d113af73f.jpg)
Frank solutions for Mathematics [English] Class 9 ICSE chapter 19 - Quadrilaterals
Shaalaa.com has the CISCE Mathematics Mathematics [English] Class 9 ICSE CISCE solutions in a manner that help students grasp basic concepts better and faster. The detailed, step-by-step solutions will help you understand the concepts better and clarify any confusion. Frank solutions for Mathematics Mathematics [English] Class 9 ICSE CISCE 19 (Quadrilaterals) include all questions with answers and detailed explanations. This will clear students' doubts about questions and improve their application skills while preparing for board exams.
Further, we at Shaalaa.com provide such solutions so students can prepare for written exams. Frank textbook solutions can be a core help for self-study and provide excellent self-help guidance for students.
Concepts covered in Mathematics [English] Class 9 ICSE chapter 19 Quadrilaterals are Introduction of Rectilinear Figures, Names of Polygons, Concept of Quadrilaterals, Diagonal Properties of Different Kinds of Parallelograms, Property: The Diagonals of a Rectangle Are of Equal Length., Property: The diagonals of a square are perpendicular bisectors of each other., Types of Quadrilaterals, Property: The Opposite Sides of a Parallelogram Are of Equal Length., Property: The Opposite Angles of a Parallelogram Are of Equal Measure., Property: The diagonals of a rhombus are perpendicular bisectors of one another..
Using Frank Mathematics [English] Class 9 ICSE solutions Quadrilaterals exercise by students is an easy way to prepare for the exams, as they involve solutions arranged chapter-wise and also page-wise. The questions involved in Frank Solutions are essential questions that can be asked in the final exam. Maximum CISCE Mathematics [English] Class 9 ICSE students prefer Frank Textbook Solutions to score more in exams.
Get the free view of Chapter 19, Quadrilaterals Mathematics [English] Class 9 ICSE additional questions for Mathematics Mathematics [English] Class 9 ICSE CISCE, and you can use Shaalaa.com to keep it handy for your exam preparation.
