Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Should the internal energy of a system necessarily increase if heat is added to it?
Solution
Change in internal energy of a system, `Delta U=C_vDeltaT`
Here,
Cv = Specific heat at constant volume
ΔT = Change in temperature.
If ΔT = 0, then ΔU = 0, i.e. in isothermal processes, where temperature remains constant, the internal energy doesn't change even on adding heat to the system.
Thus, the internal energy of a system should not necessarily increase if heat is added to it.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Explain why Two bodies at different temperatures T1 and T2, if brought in thermal contact, do not necessarily settle to the mean temperature (T1 + T2)/2.
Should the internal energy of a system necessarily increase if its temperature is increased?
When a tyre bursts, the air coming out is cooler than the surrounding air. Explain.
Figure shows two processes A and B on a system. Let ∆Q1 and ∆Q2 be the heat given to the system in processes A and B respectively. Then ____________ .
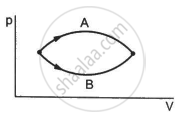
In a process on a system, the initial pressure and volume are equal to the final pressure and volume.
(a) The initial temperature must be equal to the final temperature.
(b) The initial internal energy must be equal to the final internal energy.
(c) The net heat given to the system in the process must be zero.
(d) The net work done by the system in the process must be zero.
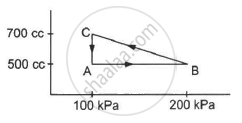
A gas is taken through a cyclic process ABCA as shown in figure. If 2.4 cal of heat is given in the process, what is the value of J ?
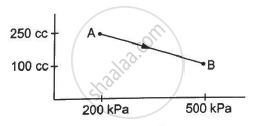
A gas is taken along the path AB as shown in figure. If 70 cal of heat is extracted from the gas in the process, calculate the change in the internal energy of the system.
A system releases 130 kJ of heat while 109 kJ of work is done on the system. Calculate the change in internal energy.
When does a system lose energy to its surroundings and its internal energy decreases?
A system releases 100 kJ of heat while 80 kJ of work is done on the system. Calculate the change in internal energy.
One gram of water (1 cm3) becomes 1671 cm3 of steam at a pressure of 1 atm. The latent heat of vaporization at this pressure is 2256 J/g. Calculate the external work and the increase in internal energy.
The internal energy of a system is ______
An ideal gas is compressed at a constant temperature. Its internal energy will ____________.
In a thermodynamic system, working substance is ideal gas. Its internal energy is in the form of ______.
In insulated systems, the amount of external work done by the gas is proportional to:
A gas is compressed at a constant pressure of 50 N/m2 from a volume of 10 m3 to a volume of 4 m3. Energy of 100 J is then added to the gas by heating. Its internal energy is ______.
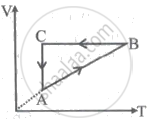
A cyclic process ABCA is shown in the V-T diagram. A process on the P-V diagram is ______.
If a gas is compressed adiabatically:
A system releases 125 kJ of heat while 104 kJ work is done on the system. Calculate the change in internal energy.
