Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
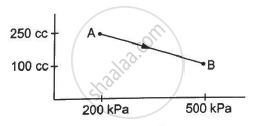
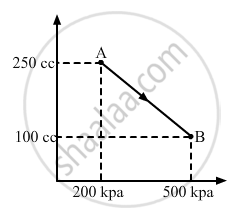
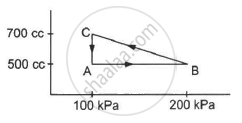
A gas is taken along the path AB as shown in figure. If 70 cal of heat is extracted from the gas in the process, calculate the change in the internal energy of the system.
Solution
Given:- 70 cal of heat is extracted from the system.
Here,
∆Q = -70 cal = -(70 × 4.2) J = -294 J
From the first law of thermodynamics, we get
∆W = P ∆ V
If P is the average pressure between points A and B and ∆V is the change in volume of the system while going from point A to B, then
∆W = `-1/2`× (200 + 500) × 103 × (150 × 10−6)
∆W = `-1/2`× 700 × 150 × 10−3
∆W = - 525 × 10−1 = - 52.5 J
Here, negative sign is taken because the final volume is less than the initial volume.
∆U = ?
∆Q = ∆U + ∆W
∆Q = - 294 J
Here, negative sign indicates that heat is extracted out from the system.
⇒ − 294 = ∆U - 52.5
⇒ ∆U = − 294 + 52.5 = - 241.5 J
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
In changing the state of a gas adiabatically from an equilibrium state A to another equilibrium state B, an amount of work equal to 22.3 J is done on the system. If the gas is taken from state A to B via a process in which the net heat absorbed by the system is 9.35 cal, how much is the net work done by the system in the latter case? (Take 1 cal = 4.19 J)
Should the internal energy of a system necessarily increase if heat is added to it?
A force F is applied on a block of mass M. The block is displaced through a distance d in the direction of the force. What is the work done by the force on the block? Does the internal energy change because of this work?
Can work be done by a system without changing its volume?
When a tyre bursts, the air coming out is cooler than the surrounding air. Explain.
Consider the process on a system shown in figure. During the process, the work done by the system ______________ .
Consider the following two statements.
(A) If heat is added to a system, its temperature must increase.
(B) If positive work is done by a system in a thermodynamic process, its volume must increase.
Consider two processes on a system as shown in figure.
The volumes in the initial states are the same in the two processes and the volumes in the final states are also the same. Let ∆W1 and ∆W2 be the work done by the system in the processes A and B respectively.
A gas is taken through a cyclic process ABCA as shown in figure. If 2.4 cal of heat is given in the process, what is the value of J ?
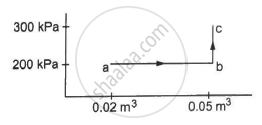
A substance is taken through the process abc as shown in figure. If the internal energy of the substance increases by 5000 J and a heat of 2625 cal is given to the system, calculate the value of J.
Define heat.
When does a system lose energy to its surroundings and its internal energy decreases?
Explain given cases related to energy transfer between the system and surrounding –
- energy transferred (Q) > 0
- energy transferred (Q) < 0
- energy transferred (Q) = 0
A thermodynamic system goes from states
(i) P, V to 2P, V (ii) P, V to P, 2V
The work done in the two cases is ____________.
8 m3 of a gas is heated at the pressure 105 N/m2 until its volume increases by 10%. Then, the external work done by the gas is ____________.
Two samples A and B, of a gas at the same initial temperature and pressure are compressed from volume V to V/2; A isothermally and B adiabatically. The final pressure of A will be ______.
Which of the following represents isothermal process?
A person of mass 60 kg wants to lose 5kg by going up and down a 10 m high stairs. Assume he burns twice as much fat while going up than coming down. If 1 kg of fat is burnt on expending 7000 kilo calories, how many times must he go up and down to reduce his weight by 5 kg?
Explain the change in internal energy of a thermodynamic system (the gas) by heating it.
