Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Solve the following question using appropriate Euclid’s axiom:
In the following figure, we have ∠1 = ∠2, ∠2 = ∠3. Show that ∠1 = ∠3.
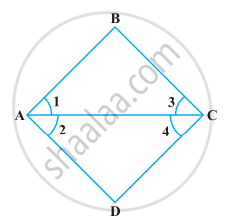
Solution
Given, ∠1 = ∠2 ...(i)
And ∠2 = ∠3 ...(ii)
According to Euclid’s axiom, things which are equal to the same thing are equal to one another.
From equations (i) and (ii),
∠1 = ∠3
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Give a definition of the following term. Are there other terms that need to be defined first? What are they, and how might you define them?
radius of a circle
If a point C lies between two points A and B such that AC = BC, then prove that AC = `1/2` AB. Explain by drawing the figure.
If a point C lies between two points A and B such that AC = BC, point C is called a mid-point of line segment AB. Prove that every line segment has one and only one mid-point.
In how many points a line, not in a plane, can intersect the plane?
The number of dimension, a point has ______.
Euclid belongs to the country ______.
Pythagoras was a student of ______.
If a quantity B is a part of another quantity A, then A can be written as the sum of B and some third quantity C.
Attempts to prove Euclid’s fifth postulate using the other postulates and axioms led to the discovery of several other geometries.
The following statement is true or false? Give reason for your answer.
In the following figure, if AB = PQ and PQ = XY, then AB = XY.

