Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Complete the chain
| Sr. No. | A | B | C |
| 1. | Expansive age pyramid | Low birth-death rate | High medical expenses |
| 2. | Constrictive age pyramid | Human capital | Unwillingness |
| 3. | Stationery age pyramid | Low number of old people | Demographic dividend |
| 4. | High working population | Problem of subsistence | Developed country |
| 5. | Migration due to drought | High number of old people | Economically backward |
Solution
| Sr. No. | A | B | C |
| 1. | Expansive age pyramid | Low number of old people | Economically backward |
| 2. | Constrictive age pyramid | High number of old people | High medical expenses |
| 3. | Stationery age pyramid | Low birth-death rate | Developed country |
| 4. | High working population | Human capital | Demographic dividend |
| 5. | Migration due to drought | Problem of subsistence | Unwillingness |
RELATED QUESTIONS
Ratio of males and females in the population is ______.
Differentiate between
Quaternary occupations and Quinary occupations
Write short note
Population pyramid and sex ratio
How is sex-ratio measured?
Describe the main characteristics of each of the major groups of human occupations in the world.
Study the given graph carefully and answer the following question:
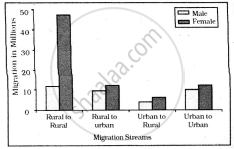
Intra-state Migration by place of Last Residence Indicating Migration Streams India, 2011
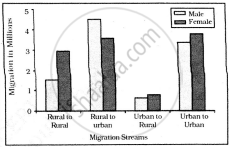
Inter-state Migration by Place of Last Residence Indicating Migration Streams India, 2011
What is the main cause of female migration from rural to urban?
The significance of age-structure is/are?
Which type of population pyramid usually characterises developed countries where population growth is zero?
A country having pyramid of population that has a wide base and sharply tapered top is characterised by which of the following?
Which one of the following is the largest linguistic group of India?
