Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
State the assumptions made for thermodynamic processes.
Solution
Assumptions made for studying various thermodynamic processes:
- The majority of the thermodynamic processes are reversible. That is, they are quasi-static in nature. They are extremely slow and the system undergoes an infinitesimal change at every stage except the adiabatic processes. The system is, therefore, in thermodynamic equilibrium during all the changes.
- The system involved in all the processes is an ideal gas enclosed in a cylinder having a movable, frictionless, and massless piston.
- The ideal gas equation is applicable to the system.
RELATED QUESTIONS
Give an example of some familiar process in which heat is added to an object, without changing its temperature.
Answer in brief.
Why should a Carnot cycle have two isothermal two adiabatic processes?
An ideal gas is taken through an isothermal process. If it does 2000 J of work on its environment, how much heat is added to it?
Draw a p-V diagram showing negative work with varying pressure.
An ideal gas of volume 2 L is adiabatically compressed to (1/10)th of its initial volume. Its initial pressure is 1.01 x 105 Pa, calculate the final pressure. (Given 𝛾 = 1.4)
Write a note on free expansion.
Explain thermodynamics of the adiabatic process.
When food is cooked in a vessel by keeping the lid closed, after some time the steam pushes the lid outward. By considering the steam as a thermodynamic system, then in the cooking process
In an isochoric process, we have ____________.
Give an expression for work done in an isothermal process.
Apply first law for an adiabatic process.
Give the equation of state for an adiabatic process.
Give an equation state for an isochoric process.
Draw the PV diagram for the isochoric process.
What is a cyclic process?
Derive the work done in an isothermal process.
What are the limitations of the first law of thermodynamics?
In a petrol engine, (internal combustion engine) air at atmospheric pressure and temperature of 20°C is compressed in the cylinder by the piston to `1/8` of its original volume. Calculate the temperature of the compressed air. (For air γ = 1.4)
An ideal gas is expanded isothermally from volume V1 to volume V2 and then compressed adiabatically to original volume V1. If the initial pressure is P1, the final pressure is P3 and net work done is W, then ____________.
An ideal gas is made to go from a state A to stale B in the given two different ways (see figure) (i) an isobaric and then an isochoric process and (ii) an isochoric and then an isobaric process. The work done by gas in the two processes are W1 and W2 respectively. Then,

Assertion: Equal volumes of monatomic and polyatomic gases are adiabatically compressed separately to equal compression ratio `("P"_2/"P"_1)`. Then monatomic gas will have greater final volume.
Reason: Among ideal gases, molecules of a monatomic gas have the smallest number of degrees of freedom.
Ideal gas for which 'ϒ' = 1.5 is suddenly compressed to `1/4`th of its initial volume. The ratio of 4 the final pressure to the initial pressure is ______.
`(ϒ = "C"_"p"/"C"_"v")`
The work done on the system in changing the state of a gas adiabatically from equilibrium state A to equilibrium state B is 22.4 J. If the gas is taken from state A to B through another process in which the net heat absorbed by the system is 15.5 cal, then the net work done by the system in the latter case is ______.
( l cal = 4.2 J)
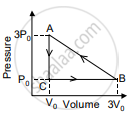
In the figure shown here, the work done in the process ACBA is ______.
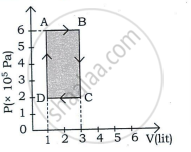
An ideal gas is taken through a cyclic process ABCDA as shown in figure. The net work done by the gas during the cycle is ______.