Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
The adjacent sides of a parallelogram are 15 cm and 10 cm. If the distance between the longer sides is 6 cm, find the distance between the shorter sides.
Solution
In parallelogram ABCD
AB = DC = 15 cm
BC = AD = 10 cm
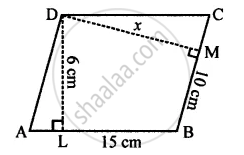
Distance between longer sides AB and DC is 6 cm
i.e., perpendicular DL = 6 cm
DM ⊥ BC
Area of parallelogram = Base × Altitude
= AB × DL = 15 × 6 = 90 cm2
Again let DM = x cm
∴ Area of parallelogram ABCD = BC × DM
= 10 × x = 10x cm2
∴ 10x cm2 = 90 cm2
⇒ x = `90/10` = 9 cm
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
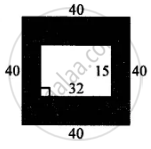
In the figure given below, find the area of shaded region: (All measurements are in cm)
The base of a parallelogram is thrice it height. If its area is 768 cm2, find the base and the height of the parallelogram.
One side of a parallelogram is 18 cm and its area is 153 cm2. Find the distance of the given side from its opposite side.
Find the area of an equilateral triangle whose each side is 16 cm. (Take `sqrt3`= 1.73)
Find the area of an isosceles triangle whose base is 16 cm and the length of each of the equal sides is 10 cm.
Find the base of a triangle whose area is 360 cm2 and height is 24 cm.
The ratio between the radius of two circles is 5 : 7. Find the ratio between their:
(i) circumference
(ii) areas
A metal wire, when bent in the form of a square of largest area, encloses an area of 484 cm2. Find the length of the wire. If the same wire is bent to the largest circle, find:
(i) radius of the circle formed.
(ii) area of the circle.
A wire is along the boundary of a circle with a radius of 28 cm. If the same wire is bent in the form of a square, find the area of the square formed.
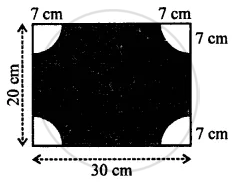
From each corner of a rectangular paper (30 cm x 20 cm) a quadrant of a circle of radius 7 cm is cut. Find the area of the remaining paper i.e., shaded portion.