Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
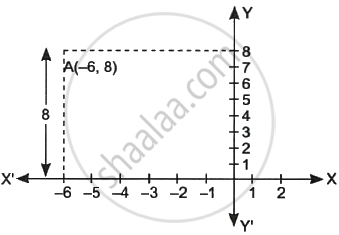
The distance of the point (–6, 8) from x-axis is ______.
Options
6 units
– 6 units
8 units
10 units
Solution
The distance of the point (–6, 8) from x-axis is 8 units.
Explanation:
The distance of the point (x, y) from x-axis is y-coordinate
∴ The distance of the point (–6, 8) from x-axis is 8 units.
RELATED QUESTIONS
If (−2, 3), (4, −3) and (4, 5) are the mid-points of the sides of a triangle, find the coordinates of its centroid.
Determine the ratio in which the point P (m, 6) divides the join of A(-4, 3) and B(2, 8). Also, find the value of m.
Find the points on the y-axis which is equidistant form the points A(6,5) and B(- 4,3)
Show that the points A(3,0), B(4,5), C(-1,4) and D(-2,-1) are the vertices of a rhombus. Find its area.
The line segment joining A( 2,9) and B(6,3) is a diameter of a circle with center C. Find the coordinates of C
The base QR of a n equilateral triangle PQR lies on x-axis. The coordinates of the point Q are (-4, 0) and origin is the midpoint of the base. Find the coordinates of the points P and R.
Show that A(-4, -7), B(-1, 2), C(8, 5) and D(5, -4) are the vertices of a
rhombus ABCD.
Show that `square` ABCD formed by the vertices A(-4,-7), B(-1,2), C(8,5) and D(5,-4) is a rhombus.
A point whose abscissa and ordinate are 2 and −5 respectively, lies in
Show that A (−3, 2), B (−5, −5), C (2,−3), and D (4, 4) are the vertices of a rhombus.
\[A\left( 6, 1 \right) , B(8, 2) \text{ and } C(9, 4)\] are three vertices of a parallelogram ABCD . If E is the mid-point of DC , find the area of \[∆\] ADE.
Write the perimeter of the triangle formed by the points O (0, 0), A (a, 0) and B (0, b).
Write the coordinates the reflections of points (3, 5) in X and Y -axes.
Write the formula for the area of the triangle having its vertices at (x1, y1), (x2, y2) and (x3, y3).
The distance between the points (a cos 25°, 0) and (0, a cos 65°) is
The ratio in which the x-axis divides the segment joining (3, 6) and (12, −3) is
The coordinates of the fourth vertex of the rectangle formed by the points (0, 0), (2, 0), (0, 3) are
Find the point on the y-axis which is equidistant from the points (5, −2) and (−3, 2).
The point at which the two coordinate axes meet is called the ______.
A tiling or tessellation of a flat surface is the covering of a plane using one or more geometric shapes, called tiles, with no overlaps and no gaps. Historically, tessellations were used in ancient Rome and in Islamic art. You may find tessellation patterns on floors, walls, paintings etc. Shown below is a tiled floor in the archaeological Museum of Seville, made using squares, triangles and hexagons.

A craftsman thought of making a floor pattern after being inspired by the above design. To ensure accuracy in his work, he made the pattern on the Cartesian plane. He used regular octagons, squares and triangles for his floor tessellation pattern
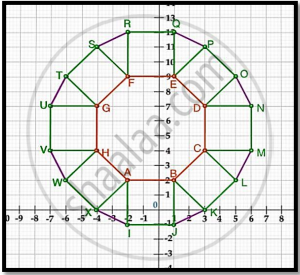
Use the above figure to answer the questions that follow:
- What is the length of the line segment joining points B and F?
- The centre ‘Z’ of the figure will be the point of intersection of the diagonals of quadrilateral WXOP. Then what are the coordinates of Z?
- What are the coordinates of the point on y-axis equidistant from A and G?
OR
What is the area of Trapezium AFGH?
