Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
The given figure gives a speed-time graph of a particle in motion along a constant direction. Three equal intervals of time are shown. In which interval is the average acceleration greatest in magnitude? In which interval is the average speed greatest? Choosing the positive direction as the constant direction of motion, give the signs of v and a in the three intervals. What are the accelerations at the points A, B, C and D?

Solution
- The average acceleration's magnitude is determined by
= `"Change in speed"/"Time interval"`
The average acceleration over a brief period of time matches the v-t graph's slope during that specific interval. The v-t graph's slope is maximum during interval 2 when compared with intervals 1 and 3, therefore the greatest average acceleration in magnitude is observed in interval 2. - Interval 3 has the highest average speed since peak D reaches the maximum on the speed axis.
- v > 0 is positive throughout all three time intervals.
- The graph's slope is positive in intervals 1 and 3, which means a > 0; thus, acceleration is positive in these intervals. Conversely, the slope is negative in interval 2, indicating a negative acceleration. Hence, a > 0 signifies a positive acceleration in intervals 1 and 3, and a < 0 indicates a negative acceleration in interval 2.
- Since the slope is zero at points A, B, C, and D, the acceleration at these points is also zero.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Read the statement below carefully and state, with reason and example, if it is true or false:
A particle in one-dimensional motion with positive value of acceleration must be speeding up.
Suggest a suitable physical situation for the following graph:
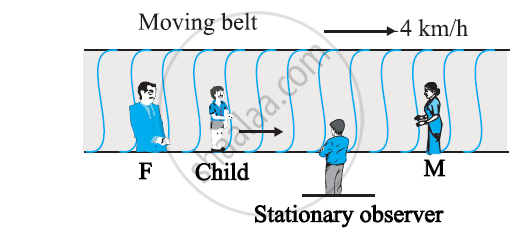
On a long horizontally moving belt (Fig. 3.26), a child runs to and fro with a speed 9 km h–1 (with respect to the belt) between his father and mother located 50 m apart on the moving belt. The belt moves with a speed of 4 km h–1. For an observer on a stationary platform outside, what is the
(a) speed of the child running in the direction of motion of the belt ?.
(b) speed of the child running opposite to the direction of motion of the belt ?
(c) time taken by the child in (a) and (b) ?
Which of the answers alter if motion is viewed by one of the parents?
Give example where the velocity is opposite in direction to the acceleration.
Give example where the velocity is perpendicular to the acceleration.
The accelerations of a particle as seen from two frames S1 and S2 have equal magnitude 4 m/s2.
An object having a velocity 4.0 m/s is accelerated at the rate of 1.2 m/s2 for 5.0 s. Find the distance travelled during the period of acceleration.
The displacement of particle is given by x = `2/lambda (1 - e^(-lambdat))`, the acceleration of particle at 2s when λ = 2s–1 will be (Take `l`n 0.018 = – 4)
Give example of a motion where x > 0, v < 0, a > 0 at a particular instant.
An object falling through a fluid is observed to have acceleration given by a = g – bv where g = gravitational acceleration and b is constant. After a long time of release, it is observed to fall with constant speed. What must be the value of constant speed?
