Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
The length and the breadth of a rectangle are 6 cm and 4 cm respectively. Find the height of a triangle whose base is 6 cm and the area is 3 times that of the rectangle.
Solution
Area of the rectangle is given by
A = l x b
= 6 x 4
= 24 sq . cm
Let h be the height of the triangle ,then
`1/2 xx "base" xx h = 3"A"`
`1/2 xx 6 xx h = 3 xx 24`
h = 24 cm
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
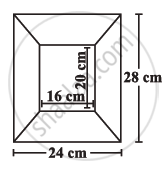
Diagram of the adjacent picture frame has outer dimensions = 24 cm × 28 cm and inner dimensions 16 cm × 20 cm. Find the area of each section of the frame, if the width of each section is same.
The distance between parallel sides of a trapezium is 15 cm and the length of the line segment joining the mid-points of its non-parallel sides is 26 cm. Find the area of the trapezium.
A wire when bent in the form of a square encloses an area = 576 cm2. Find the largest area enclosed by the same wire when bent to form;
(i) an equilateral triangle.
(ii) A rectangle whose adjacent sides differ by 4 cm.
Calculate the area of quadrilateral ABCD, in which ∠ABD = 90°, triangle BCD is an equilateral triangle of side 24 cm and AD = 26 cm.
A rectangular plot 85 m long and 60 m broad is to be covered with grass leaving 5 m all around. Find the area to be laid with grass.
The perimeter of a rhombus is 52 cm. If one diagonal is 24 cm; find:
(i) The length of its other diagonal,
(ii) Its area.
Two adjacent sides of a parallelogram are 24 cm and 18 cm. If the distance between the longer sides is 12 cm; find the distance between the shorter sides.
Vertices of given triangles are taken in order and their areas are provided aside. Find the value of ‘p’.
| Vertices | Area (sq.units) |
| (0, 0), (p, 8), (6, 2) | 20 |
Find the area of the quadrilateral whose vertices are at (– 9, – 2), (– 8, – 4), (2, 2) and (1, – 3)
Find the value of k, if the area of a quadrilateral is 28 sq. units, whose vertices are (– 4, – 2), (– 3, k), (3, – 2) and (2, 3)
