Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
The molecules having dipole moment are:
(i) 2,2-Dimethylpropane
(ii) trans-Pent-2-ene
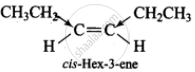
(iii) cis-Hex-3-ene
(iv) 2, 2, 3, 3 - Tetramethylbutane.
Solution
(ii) trans-Pent-2-ene
(iii) cis-Hex-3-ene
Explanation:
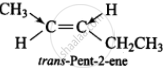
Since, the +1 effect of CH2CH3 group is higher than that of CH3 group, therefore, the dipole moments of C – CH3 and C – CH2CH3 bonds are unequal. Although these two dipoles oppose each other, yet they do not exactly cancel out each other and hence trans-2-pentene has small but finite dipole moment.
In cis-hex-3-ene, although the dipole moments of the two C – CH2CH3 bond are equal, but they are inclined to each other at an angle of 60° and hence have a finite dipole moment.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Draw the cis and trans structures of hex-2-ene. Which isomer will have higher b.p. and why?
What effect does branching of an alkane chain has on its boiling point?
What is the relationship between the members of following pairs of structures? Are they structural or geometrical isomers or resonance contributors?
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{D}\phantom{......}\ce{H}\\
\backslash\phantom{......}/\\
\ce{C = C}\\
\phantom{...}/\phantom{......}\backslash\phantom{...}\\\ce{H}\phantom{.......}\ce{D}
\end{array}\]
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{D}\phantom{......}\ce{D}\\
\backslash\phantom{......}/\\
\ce{C = C}\\
\phantom{...}/\phantom{......}\backslash\phantom{...}\\\ce{H}\phantom{.......}\ce{H}\end{array}\]
Find out the type of isomerism exhibited by the following pair.
Find out the type of isomerism exhibited by the following pair.

Choose the correct option.
Which type of isomerism is possible in CH3 CHCHCH3?
Molecular formula of the functional isomer of methyl formate is ____________.
What type(s) of isomerism is(are) shown by [Co(NH3)4Br2]Cl?
Which of the following is a functional isomer of pentan-2-ol?
What is the relationship between the members of following pairs of structures? Are they structural or geometrical isomers or resonance contributors?
\[\begin{array}{cc}\ce{^+OH}\\||\\
\ce{H - C - OH}\end{array}\]
\[\begin{array}{cc}\ce{OH}\phantom{.}\\|\phantom{...}\\
\ce{H - C^+ - OH}\end{array}\]
Which of the following pairs are not functional group isomers?
| I. | \[\begin{array}{cc} \phantom{.......................}\ce{O}\\ \phantom{.......................}||\\ \ce{CH3 - CH2 - CH2 - CH2 - C - H} \end{array}\] |
| II. | \[\begin{array}{cc} \phantom{.................}\ce{O}\\ \phantom{.................}||\\ \ce{CH3 - CH2 - CH2 - C - H} \end{array}\] |
| III. | \[\begin{array}{cc} \ce{CH3 - CH2 - C - CH2 - CH3}\\ \phantom{}||\\ \phantom{}\ce{O} \end{array}\] |
| IV. | \[\begin{array}{cc} \ce{CH3 - CH - CH2 - C - H}\\ \phantom{...}|\phantom{............}||\phantom{}\\ \phantom{...}\ce{CH3}\phantom{.........}\ce{O}\phantom{} \end{array}\] |
(i) II and III
(ii) II and IV
(iii) I and IV
(iv) I and II
Consider structures I to VII and answer the question:
| I. | CH3 – CH2 – CH2 – CH2 – OH |
| II. | \[\begin{array}{cc} \ce{CH3 - CH2 - CH - CH3}\\ \phantom{.....}|\\ \phantom{.......}\ce{OH} \end{array}\] |
| III. | \[\begin{array}{cc} \phantom{...}\ce{CH3}\\ \phantom{}|\\ \ce{CH3 - C - CH3}\\ \phantom{}|\\ \phantom{..}\ce{OH} \end{array}\] |
| IV. | \[\begin{array}{cc} \ce{CH3 - CH - CH2 - OH}\\ |\phantom{........}\\ \ce{CH3}\phantom{......} \end{array}\] |
| V. | CH3 – CH2 – O – CH2 – CH3 |
| VI. | CH3 – O – CH2 – CH2 – CH3 |
| VII. | \[\begin{array}{cc} \ce{CH3 - O - CH - CH3}\\ \phantom{...}|\\ \phantom{......}\ce{CH3} \end{array}\] |
Identify the pairs of compounds that represents chain isomerism.
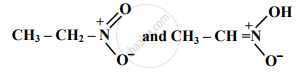
Compounds with same molecular formula but differing in their structures are said to be structural isomers. What type of structural isomerism is shown by
CH3 – S – CH2 – CH2 – CH3
And
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\phantom{.....................}\ce{CH3}\\
\phantom{................}/\\
\phantom{}\ce{CH3 - S - CH}\\
\phantom{...............}\backslash\\
\phantom{....................}\ce{CH3}
\end{array}\]
Assertion (A): The compound cyclooctane has the following structural formula: ![]()
It is cyclic and has conjugated 8π-electron system but it is not an aromatic compound.
Reason (R): (4n + 2)π electrons rule does not hold good and ring is not planar.
Tautomerism is exhibited by ______.
Ether and alcohol are ______.
Which type of isomerism can not be shown by benzaldoxime?
Which one of the following pairs are called position isomers?
The number of acyclic structural isomers (including geometrical isomers) for pentene are ______.
