Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
The number of silicon atoms per m3 is 5 × 1028. This is doped simultaneously with 5 × 1022 atoms per m3 of Arsenic and 5 × 1020 per m3 atoms of Indium. Calculate the number of electrons and holes. Given that ni= 1.5 × 1016 m−3. Is the material n-type or p-type?
Solution
Number of silicon atoms, N = 5 × 1028 atoms/m3
Number of arsenic atoms, nAs = 5 × 1022 atoms/m3
Number of indium atoms, nIn = 5 × 1020 atoms/m3
Number of thermally-generated electrons, ni = 1.5 × 1016 electrons/m3
Number of electrons, ne = 5 × 1022 − 1.5 × 1016 ≈ 4.99 × 1022
Number of holes = nh
In thermal equilibrium, the concentrations of electrons and holes in a semiconductor are related as:
nenh = ni2
`therefore "n"_"h" = ("n"_"i"^2)/"n"_"e"`
`= (1.5 xx 10^16)^2/(4.99 xx 10^22) ~~ 4.51 xx 10^9`
Therefore, the number of electrons is approximately 4.99 × 1022 and the number of holes is about 4.51 × 109. Since the number of electrons is more than the number of holes, the material is an n-type semiconductor.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
In a p-type semiconductor, the acceptor impurity produces an energy level ______
When p-n junction diode is forward biased, then ______.
In n-type semiconductor majority carriers and minority carriers are respectively ______.
In p-type semiconductor, the dopant is ______.
The electron and hole concentration in a semiconductor in thermal equilibrium is given by ______.
State how a p-type semiconductor will be obtained from a pure crystal of a semiconductor.
Explain the following term:
Extrinsic semiconductor
Distinguish between n-type and p-type semiconductors.
In a pure semiconductor crystal of Si, if antimony is added then what type of extrinsic semiconductor is obtained. Draw the energy band diagram of this extrinsic semiconductor so formed.
The conductivity of a semiconductor increases with increase in temperature because ______.
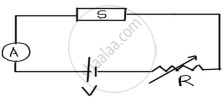
The figure shows a piece of pure semiconductor S in series with a variable resistor R and a source of constant voltage V. Should the value of R be increased or decreased to keep the reading of the ammeter constant, when semiconductor S is heated? Justify your answer
Two crystals C1 and C2, made of pure silicon, are doped with arsenic and aluminium respectively.
Identify the extrinsic semiconductors so formed.
Name the extrinsic semiconductors formed when pure germanium is doped with a trivalent impurity. Draw the energy band diagram of extrinsic semiconductors so formed.
Name the extrinsic semiconductors formed when pure germanium is doped with a Pentavalent impurity. Draw the energy band diagram of extrinsic semiconductors so formed.
In an extrinsic semiconductor, the number density of holes is 4 × 1020 m-3. If the number density of intrinsic carriers is 1.2 × 1015 m-3, the number density of electrons in it is ______.
- Assertion (A): Putting the p-type semiconductor slab directly in physical contact with the n-type semiconductor slab cannot form the pn junction.
- Reason (R): The roughness at contact will be much more than inter atomic crystal spacing and continuous flow of charge carriers is not possible.
With an increase in the temperature, the electrical conductivity of a semiconductor ______.
What type of semiconductor is obtained when a crystal of silicon is doped with a trivalent element?
