Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
The velocity of a particle is towards west at an instant. Its acceleration is not towards west, not towards east, not towards north and towards south. Give an example of this type of motion .
Solution
Motion of a projectile at the highest point of its path: Because at this point, the projectile has only horizontal component of velocity. So, it can have velocity towards west and acceleration in the vertically downward direction.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Two trains A and B of length 400 m each are moving on two parallel tracks with a uniform speed of 72 km h–1 in the same direction, with A ahead of B. The driver of B decides to overtake A and accelerates by 1 m/s2. If after 50 s, the guard of B just brushes past the driver of A, what was the original distance between them?
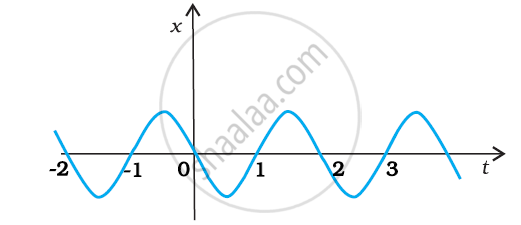
The following figure gives the x-t plot of a particle executing one-dimensional simple harmonic motion. Give the signs of position, velocity and acceleration variables of the particle at t = 0.3 s, 1.2 s, – 1.2 s.
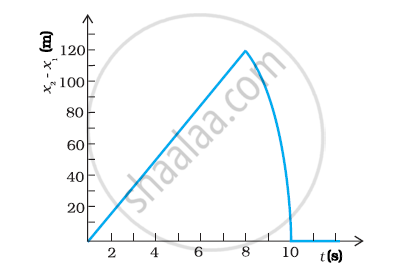
Two stones are thrown up simultaneously from the edge of a cliff 200 m high with initial speeds of 15 m/s and 30 m/s. Verify that the graph shown in Fig. 3.27 correctly represents the time variation of the relative position of the second stone with respect to the first. Neglect air resistance and assume that the stones do not rebound after hitting the ground. Take g = 10 m/s2. Give the equations for the linear and curved parts of the plot.
A person travelling at 43.2 km/h applies the brake giving a deceleration of 6.0 m/s2 to his scooter. How far will it travel before stopping?
A bullet travelling with a velocity of 16 m/s penetrates a tree trunk and comes to rest in 0.4 m. Find the time taken during the retardation.
A particle starting from rest moves with constant acceleration. If it takes 5.0 s to reach the speed 18.0 km/h find the distance travelled by the particle during this period.
A driver takes 0.20 s to apply the brakes after he sees a need for it. This is called the reaction time of the driver. If he is driving a car at a speed of 54 km/h and the brakes cause a deceleration of 6.0 m/s2, find the distance travelled by the car after he sees the need to put the brakes on.
A car travelling at 60 km/h overtakes another car travelling at 42 km/h. Assuming each car to be 5.0 m long, find the time taken during the overtake and the total road distance used for the overtake.
A ball is dropped from a balloon going up at a speed of 7 m/s. If the balloon was at a height 60 m at the time of dropping the ball, how long will the ball take in reaching the ground?
An NCC parade is going at a uniform speed of 6 km/h through a place under a berry tree on which a bird is sitting at a height of 12.1 m. At a particular instant the bird drops a berry. Which cadet (give the distance from the tree at the instant) will receive the berry on his uniform?
A ball is dropped from a height. If it takes 0.200 s to cross the last 6.00 m before hitting the ground, find the height from which it was dropped. Take g = 10 m/s2.
A ball is dropped from a height of 5 m onto a sandy floor and penetrates the sand up to 10 cm before coming to rest. Find the retardation of the ball is sand assuming it to be uniform.
In a soccer practice session the football is kept at the centre of the filed 40 yards from the 10 ft high goalposts. A goal is attempted by kicking the football at a speed of 64 ft/s at an angle of 45° to the horizontal. Will the ball reach the goal post?
A popular game in Indian villages is goli which is played with small glass balls called golis. The goli of one player is situated at a distance of 2.0 m from the goli of the second player. This second player has to project his goli by keeping the thumb of the left hand at the place of his goli, holding the goli between his two middle fingers and making the throw. If the projected goli hits the goli of the first player, the second player wins. If the height from which the goli is projected is 19.6 cm from the ground and the goli is to be projected horizontally, with what speed should it be projected so that it directly hits the stationery goli without falling on the ground earlier?
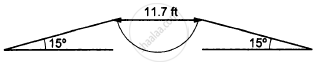
In the following figure shows a 11.7 ft wide ditch with the approach roads at an angle of 15° with the horizontal. With what minimum speed should a motorbike be moving on the road so that it safely crosses the ditch?
Assume that the length of the bike is 5 ft, and it leaves the road when the front part runs out of the approach road.
Find the average velocity of a projectile between the instants it crosses half the maximum height. It is projected with a speed u at an angle θ with the horizontal.
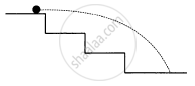
A staircase contains three steps each 10 cm high and 20 cm wide (in the following figure). What should be the minimum horizontal velocity of a ball rolling of the uppermost plane so as to hit directly the lowest plane ?
A river 400 m wide is flowing at a rate of 2.0 m/s. A boat is sailing at a velocity of 10 m/s with respect to the water, in a direction perpendicular to the river. How far from the point directly opposite to the starting point does the boat reach the opposite bank?
Two friends A and B are standing a distance x apart in an open field and wind is blowing from A to B. A beat a drum and B hears the sound t1 time after he sees the event. A and B interchange their positions and the experiment is repeated. This time B hears the drum timer after he sees the event. Calculate the velocity of sound in still air v and the velocity of wind u. Neglect the time light takes in travelling between the friends.
A man is standing on top of a building 100 m high. He throws two balls vertically, one at t = 0 and other after a time interval (less than 2 seconds). The later ball is thrown at a velocity of half the first. The vertical gap between first and second ball is +15 m at t = 2 s. The gap is found to remain constant. Calculate the velocity with which the balls were thrown and the exact time interval between their throw.
