Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
There are two types of fertilisers 'A' and 'B'. 'A' consists of 12% nitrogen and 5% phosphoric acid whereas 'B' consists of 4% nitrogen and 5% phosphoric acid. After testing the soil conditions, farmer finds that he needs at least 12 kg of nitrogen and 12 kg of phosphoric acid for his crops. If 'A' costs Rs 10 per kg and 'B' cost Rs 8 per kg, then graphically determine how much of each type of fertiliser should be used so that nutrient requirements are met at a minimum cost
Solution
| Fertilizer | Nitrogen | Phosphoric Acid | Cost/kg (in Rs) |
| A | 12% | 5% | 10 |
| B | 4% | 5% | 8 |
Let the requirement of fertilizer A by the farmer be x kg and that of B be y kg.
Given that farmer requires atleast 12 kg of nitrogen and 12 kg of phosphoric acid for his crops.
The inequations thus formed based on the given problem will be as follows:
`12/100x + 4/100y ≥ 12`
⇒12x + 4y ≥ 1200
⇒3x + y ≥ 300 .....(1)
Also,`(5x)/100 + (5y)/100≥12`
⇒5x + 5y ≥ 1200
⇒ x + y ≥ 240 .....(2)
x≥0 and y≥0 .....(3)
Total cost of the fertilizer Z = 10x + 8y
To solve the LPP graphically, we convert the inequations into equations to obtain the following lines:
3x + y = 300
x + y = 240
x = 0
y = 0
Based on the above equations the graph obtained will be:
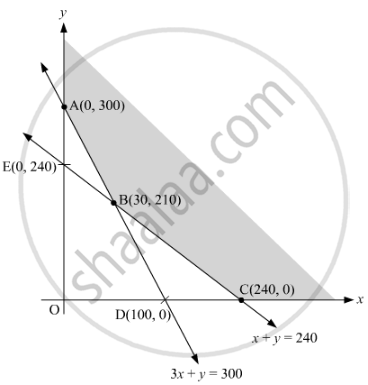
| Corner points | Z | |
| A | (0, 300) | 2400 |
| C | (240, 0) | 2400 |
| B | (30, 210) | 1980 |
From the table, it is clear that the minimum value of Z is obtained at C(30, 210). The minimum value of Z is 1980.So, the minimum requirement of fertilizer of type A will be 30 kg and that of type B will be 210 kg.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Solve the following LPP by using graphical method.
Maximize : Z = 6x + 4y
Subject to x ≤ 2, x + y ≤ 3, -2x + y ≤ 1, x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0.
Also find maximum value of Z.
A dealer in rural area wishes to purchase a number of sewing machines. He has only Rs 5,760 to invest and has space for at most 20 items for storage. An electronic sewing machine cost him Rs 360 and a manually operated sewing machine Rs 240. He can sell an electronic sewing machine at a profit of Rs 22 and a manually operated sewing machine at a profit of Rs 18. Assuming that he can sell all the items that he can buy, how should he invest his money in order to maximize his profit? Make it as a LPP and solve it graphically.
Maximise Z = x + 2y subject to the constraints
`x + 2y >= 100`
`2x - y <= 0`
`2x + y <= 200`
Solve the above LPP graphically
Solve the following LPP by graphical method:
Minimize Z = 7x + y subject to 5x + y ≥ 5, x + y ≥ 3, x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0
Maximize Z = 4x + 3y
subject to
\[3x + 4y \leq 24\]
\[8x + 6y \leq 48\]
\[ x \leq 5\]
\[ y \leq 6\]
\[ x, y \geq 0\]
Minimize Z = 2x + 4y
Subject to
\[x + y \geq 8\]
\[x + 4y \geq 12\]
\[x \geq 3, y \geq 2\]
Minimize Z = 30x + 20y
Subject to
\[x + y \leq 8\]
\[ x + 4y \geq 12\]
\[5x + 8y = 20\]
\[ x, y \geq 0\]
To maintain one's health, a person must fulfil certain minimum daily requirements for the following three nutrients: calcium, protein and calories. The diet consists of only items I and II whose prices and nutrient contents are shown below:
| Food I | Food II | Minimum daily requirement | |
| Calcium Protein Calories |
10 5 2 |
4 6 6 |
20 20 12 |
| Price | Rs 0.60 per unit | Rs 1.00 per unit |
Find the combination of food items so that the cost may be minimum.
One kind of cake requires 200 g of flour and 25 g of fat, and another kind of cake requires 100 g of flour and 50 g of fat. Find the maximum number of cakes which can be made from 5 kg of flour and 1 kg of fat assuming that there is no storage of the other ingredients used in making the cakes.
If a young man drives his vehicle at 25 km/hr, he has to spend Rs 2 per km on petrol. If he drives it at a faster speed of 40 km/hr, the petrol cost increases to Rs 5/per km. He has Rs 100 to spend on petrol and travel within one hour. Express this as an LPP and solve the same.
A manufacturer has three machines installed in his factory. machines I and II are capable of being operated for at most 12 hours whereas Machine III must operate at least for 5 hours a day. He produces only two items, each requiring the use of three machines. The number of hours required for producing one unit each of the items on the three machines is given in the following table:
| Item | Number of hours required by the machine | ||
A B |
I | II | III |
| 1 2 |
2 1 |
1 5/4 |
|
He makes a profit of Rs 6.00 on item A and Rs 4.00 on item B. Assuming that he can sell all that he produces, how many of each item should he produces so as to maximize his profit? Determine his maximum profit. Formulate this LPP mathematically and then solve it.
A company produces two types of leather belts, say type A and B. Belt A is a superior quality and belt B is of a lower quality. Profits on each type of belt are Rs 2 and Rs 1.50 per belt, respectively. Each belt of type A requires twice as much time as required by a belt of type B. If all belts were of type B, the company could produce 1000 belts per day. But the supply of leather is sufficient only for 800 belts per day (both A and B combined). Belt A requires a fancy buckle and only 400 fancy buckles are available for this per day. For belt of type B, only 700 buckles are available per day.
How should the company manufacture the two types of belts in order to have a maximum overall profit?
A manufacturer makes two types A and B of tea-cups. Three machines are needed for the manufacture and the time in minutes required for each cup on the machines is given below:
| Machines | |||
| I | II | III | |
| A B |
12 6 |
18 0 |
6 9 |
Each machine is available for a maximum of 6 hours per day. If the profit on each cup A is 75 paise and that on each cup B is 50 paise, show that 15 tea-cups of type A and 30 of type B should be manufactured in a day to get the maximum profit.
An aeroplane can carry a maximum of 200 passengers. A profit of Rs 400 is made on each first class ticket and a profit of Rs 600 is made on each economy class ticket. The airline reserves at least 20 seats of first class. However, at least 4 times as many passengers prefer to travel by economy class to the first class. Determine how many each type of tickets must be sold in order to maximize the profit for the airline. What is the maximum profit.
A man owns a field of area 1000 sq.m. He wants to plant fruit trees in it. He has a sum of Rs 1400 to purchase young trees. He has the choice of two types of trees. Type A requires 10 sq.m of ground per tree and costs Rs 20 per tree and type B requires 20 sq.m of ground per tree and costs Rs 25 per tree. When fully grown, type A produces an average of 20 kg of fruit which can be sold at a profit of Rs 2.00 per kg and type B produces an average of 40 kg of fruit which can be sold at a profit of Rs. 1.50 per kg. How many of each type should be planted to achieve maximum profit when the trees are fully grown? What is the maximum profit?
If a young man drives his vehicle at 25 km/hr, he has to spend ₹2 per km on petrol. If he drives it at a faster speed of 40 km/hr, the petrol cost increases to ₹5 per km. He has ₹100 to spend on petrol and travel within one hour. Express this as an LPP and solve the same.
A small firm manufactures gold rings and chains. The total number of rings and chains manufactured per day is at most 24. It takes 1 hour to make a ring and 30 minutes to make a chain. The maximum number of hours available per day is 16. If the profit on a ring is Rs 300 and that on a chain is Rs 190, find the number of rings and chains that should be manufactured per day, so as to earn the maximum profit. Make it as an LPP and solve it graphically.
There are two types of fertilizers F1 and F2. F1 consists of 10% nitrogen and 6% phosphoric acid and F2 consists of 5% nitrogen and 10% phosphoric acid. After testing the soil conditions, a farmer finds the she needs atleast 14 kg of nitrogen and 14 kg of phosphoric acid for her crop. If F1 costs ₹6/kg and F2 costs ₹5/kg, determine how much of each type of fertilizer should be used so that the nutrient requirements are met at minimum cost. What is the minimum cost?
A company manufactures two types of cardigans: type A and type B. It costs ₹ 360 to make a type A cardigan and ₹ 120 to make a type B cardigan. The company can make at most 300 cardigans and spend at most ₹ 72000 a day. The number of cardigans of type B cannot exceed the number of cardigans of type A by more than 200. The company makes a profit of ₹ 100 for each cardigan of type A and ₹ 50 for every cardigan of type B.
Formulate this problem as a linear programming problem to maximize the profit to the company. Solve it graphically and find the maximum profit.
For L.P.P. maximize z = 4x1 + 2x2 subject to 3x1 + 2x2 ≥ 9, x1 - x2 ≤ 3, x1 ≥ 0, x2 ≥ 0 has ______.
The feasible region of an LPP is shown in the figure. If z = 3x + 9y, then the minimum value of z occurs at ______.
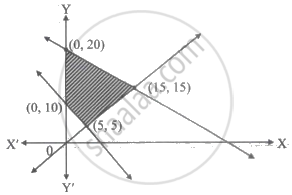
If 4x + 5y ≤ 20, x + y ≥ 3, x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0, maximum 2x + 3y is ______.
Let R be the feasible region (convex polygon) for a linear programming problem and let Z = ax + by be the objective function. When Z has an optimal value (maximum or minimum), where the variables x and y are subject to constraints described by linear inequalities,
A feasible solution to a linear programming problem
The solution set of the inequality 3x + 5y < 4 is ______.
The constraints –x1 + x2 ≤ 1, –x1 + 3x2 ≤ 9, x1x2 ≥ 0 define on ______.
Solve the following Linear Programming Problem graphically.
Maximise Z = 5x + 2y subject to:
x – 2y ≤ 2,
3x + 2y ≤ 12,
– 3x + 2y ≤ 3,
x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0
A linear programming problem is given by Z = px + qy where p, q > 0 subject to the constraints: x + y ≤ 60, 5x + y ≤ 100, x ≥ 0 and y ≥ 0
- Solve graphically to find the corner points of the feasible region.
- If Z = px + qy is maximum at (0, 60) and (10, 50), find the relation of p and q. Also mention the number of optimal solution(s) in this case.
