Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A company manufactures two types of cardigans: type A and type B. It costs ₹ 360 to make a type A cardigan and ₹ 120 to make a type B cardigan. The company can make at most 300 cardigans and spend at most ₹ 72000 a day. The number of cardigans of type B cannot exceed the number of cardigans of type A by more than 200. The company makes a profit of ₹ 100 for each cardigan of type A and ₹ 50 for every cardigan of type B.
Formulate this problem as a linear programming problem to maximize the profit to the company. Solve it graphically and find the maximum profit.
Solution
Let number of cardigans of type A and type B be x and y respectively.
To maximize : Z = 100x + 50y in ₹.
Subject to constraints: x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0,
x + y ≤ 300,
360x + 120y ≤ 72000
⇒ 3x + y ≤ 600,
y ≤ x + 200
⇒ y - x ≤ 200
| Corner Points | Value of Z (in ₹) |
| O(0, 0) | 0 |
| A(200, 0) | 20000 |
| B(150, 150) | 22500← Max. value |
| C(50, 250) | 17500 |
| D(0, 200) | 10000 |
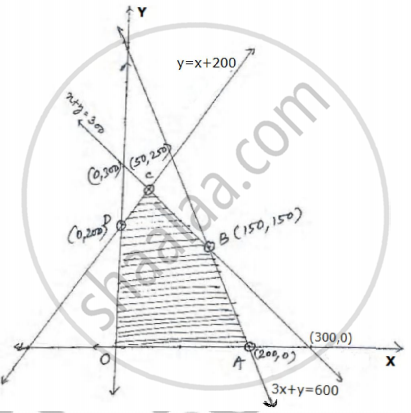
Hence no. of cardigans of type A = 150
and no. of cardigans of type B = 150.
Also, maximum profit is ₹22500.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A company manufactures bicycles and tricycles each of which must be processed through machines A and B. Machine A has maximum of 120 hours available and machine B has maximum of 180 hours available. Manufacturing a bicycle requires 6 hours on machine A and 3 hours on machine B. Manufacturing a tricycle requires 4 hours on machine A and 10 hours on machine B.
If profits are Rs. 180 for a bicycle and Rs. 220 for a tricycle, formulate and solve the L.P.P. to determine the number of bicycles and tricycles that should be manufactured in order to maximize the profit.
Maximise Z = x + 2y subject to the constraints
`x + 2y >= 100`
`2x - y <= 0`
`2x + y <= 200`
Solve the above LPP graphically
A dietician wishes to mix two kinds ·of food X· and Y in such a way that the mixture contains at least 10 units of vitamin A, 12 units of vitamin B arid 8 units of vitamin C. The vitamin contents of one kg food is given below:
| Food | Vitamin A | Vitamin.B | Vitamin C |
| X | 1 unit | 2 unit | 3 unit |
| Y | 2 unit | 2 unit | 1 unit |
Orie kg of food X costs Rs 24 and one kg of food Y costs Rs 36. Using Linear Programming, find the least cost of the total mixture. which will contain the required vitamins.
In order to supplement daily diet, a person wishes to take X and Y tablets. The contents (in milligrams per tablet) of iron, calcium and vitamins in X and Y are given as below :
| Tablets | Iron | Calcium | Vitamin |
| x | 6 | 3 | 2 |
| y | 2 | 3 | 4 |
The person needs to supplement at least 18 milligrams of iron, 21 milligrams of calcium and 16 milligrams of vitamins. The price of each tablet of X and Y is Rs 2 and Rs 1 respectively. How many tablets of each type should the person take in order to satisfy the above requirement at the minimum cost? Make an LPP and solve graphically.
Maximize Z = 5x + 3y
Subject to
\[3x + 5y \leq 15\]
\[5x + 2y \leq 10\]
\[ x, y \geq 0\]
Maximize Z = 15x + 10y
Subject to
\[3x + 2y \leq 80\]
\[2x + 3y \leq 70\]
\[ x, y \geq 0\]
Minimize Z = 3x1 + 5x2
Subject to
\[x_1 + 3 x_2 \geq 3\]
\[ x_1 + x_2 \geq 2\]
\[ x_1 , x_2 \geq 0\]
Maximize Z = −x1 + 2x2
Subject to
\[- x_1 + 3 x_2 \leq 10\]
\[ x_1 + x_2 \leq 6\]
\[ x_1 - x_2 \leq 2\]
\[ x_1 , x_2 \geq 0\]
Maximize Z = x + y
Subject to
\[- 2x + y \leq 1\]
\[ x \leq 2\]
\[ x + y \leq 3\]
\[ x, y \geq 0\]
A dietician mixes together two kinds of food in such a way that the mixture contains at least 6 units of vitamin A, 7 units of vitamin B, 11 units of vitamin C and 9 units of vitamin D. The vitamin contents of 1 kg of food X and 1 kg of food Y are given below:
| Vitamin A |
Vitamin B |
Vitamin |
Vitamin D |
|
| Food X Food Y |
1 2 |
1 1 |
1 3 |
2 1 |
One kg food X costs Rs 5, whereas one kg of food Y costs Rs 8. Find the least cost of the mixture which will produce the desired diet.
Kellogg is a new cereal formed of a mixture of bran and rice that contains at least 88 grams of protein and at least 36 milligrams of iron. Knowing that bran contains 80 grams of protein and 40 milligrams of iron per kilogram, and that rice contains 100 grams of protein and 30 milligrams of iron per kilogram, find the minimum cost of producing this new cereal if bran costs Rs 5 per kg and rice costs Rs 4 per kg
A dietician has to develop a special diet using two foods P and Q. Each packet (containing 30 g) of food P contains 12 units of calcium, 4 units of iron, 6 units of cholesterol and 6 units of vitamin A. Each packet of the same quantity of food Q contains 3 units of calcium, 20 units of iron, 4 units of cholesterol and 3 units of vitamin A. The diet requires atleast 240 units of calcium, atleast 460 units of iron and at most 300 units of cholesterol. How many packets of each food should be used to minimise the amount of vitamin A in the diet? What is the minimum of vitamin A.
A firm manufacturing two types of electric items, A and B, can make a profit of Rs 20 per unit of A and Rs 30 per unit of B. Each unit of A requires 3 motors and 4 transformers and each unit of B requires 2 motors and 4 transformers. The total supply of these per month is restricted to 210 motors and 300 transformers. Type B is an export model requiring a voltage stabilizer which has a supply restricted to 65 units per month. Formulate the linear programing problem for maximum profit and solve it graphically.
A manufacturer of patent medicines is preparing a production plan on medicines, A and B. There are sufficient raw materials available to make 20000 bottles of A and 40000 bottles of B, but there are only 45000 bottles into which either of the medicines can be put. Further, it takes 3 hours to prepare enough material to fill 1000 bottles of A, it takes 1 hour to prepare enough material to fill 1000 bottles of B and there are 66 hours available for this operation. The profit is Rs 8 per bottle for A and Rs 7 per bottle for B. How should the manufacturer schedule his production in order to maximize his profit?
A gardener has supply of fertilizer of type I which consists of 10% nitrogen and 6% phosphoric acid and type II fertilizer which consists of 5% nitrogen and 10% phosphoric acid. After testing the soil conditions, he finds that he needs at least 14 kg of nitrogen and 14 kg of phosphoric acid for his crop. If the type I fertilizer costs 60 paise per kg and type II fertilizer costs 40 paise per kg, determine how many kilograms of each fertilizer should be used so that nutrient requirements are met at a minimum cost. What is the minimum cost?
A man owns a field of area 1000 sq.m. He wants to plant fruit trees in it. He has a sum of Rs 1400 to purchase young trees. He has the choice of two types of trees. Type A requires 10 sq.m of ground per tree and costs Rs 20 per tree and type B requires 20 sq.m of ground per tree and costs Rs 25 per tree. When fully grown, type A produces an average of 20 kg of fruit which can be sold at a profit of Rs 2.00 per kg and type B produces an average of 40 kg of fruit which can be sold at a profit of Rs. 1.50 per kg. How many of each type should be planted to achieve maximum profit when the trees are fully grown? What is the maximum profit?
A cottage industry manufactures pedestal lamps and wooden shades, each requiring the use of grinding/cutting machine and sprayer. It takes 2 hours on the grinding/cutting machine and 3 hours on the sprayer to manufacture a pedestal lamp while it takes 1 hour on the grinding/cutting machine and 2 hours on the sprayer to manufacture a shade. On any day, the sprayer is available for at most 20 hours and the grinding/cutting machine for at most 12 hours. The profit from the sale of a lamp is ₹5.00 and a shade is ₹3.00. Assuming that the manufacturer sell all the lamps and shades that he produces, how should he schedule his daily production in order to maximise his profit?
A producer has 30 and 17 units of labour and capital respectively which he can use to produce two type of goods x and y. To produce one unit of x, 2 units of labour and 3 units of capital are required. Similarly, 3 units of labour and 1 unit of capital is required to produce one unit of y. If x and y are priced at Rs 100 and Rs 120 per unit respectively, how should be producer use his resources to maximize the total revenue? Solve the problem graphically.
A manufacturer makes two products, A and B. Product A sells at Rs 200 each and takes 1/2 hour to make. Product B sells at Rs 300 each and takes 1 hour to make. There is a permanent order for 14 units of product A and 16 units of product B. A working week consists of 40 hours of production and the weekly turn over must not be less than Rs 10000. If the profit on each of product A is Rs 20 and an product B is Rs 30, then how many of each should be produced so that the profit is maximum? Also find the maximum profit.
An oil company has two depots, A and B, with capacities of 7000 litres and 4000 litres respectively. The company is to supply oil to three petrol pumps, D, E, F whose requirements are 4500, 3000 and 3500 litres respectively. The distance (in km) between the depots and petrol pumps is given in the following table:
Figure
Assuming that the transportation cost per km is Rs 1.00 per litre, how should the delivery be scheduled in order that the transportation cost is minimum?
There are two types of fertilisers 'A' and 'B' . 'A' consists of 12% nitrogen and 5% phosphoric acid whereas 'B' consists of 4% nitrogen and 5% phosphoric acid. After testing the soil conditions, farmer finds that he needs at least 12 kg of nitrogen and 12 kg of phosphoric acid for his crops. If 'A' costs ₹10 per kg and 'B' cost ₹8 per kg, then graphically determine how much of each type of fertiliser should be used so that nutrient requiremnets are met at a minimum cost
A small firm manufactures necklaces and bracelets. The total number of necklaces and bracelets that it can handle per day is at most 24. It takes one hour to make a bracelet and half an hour to make a necklace. The maximum number of hours available per day is 16. If the profit on a necklace is Rs 100 and that on a bracelet is Rs 300. Formulate on L.P.P. for finding how many of each should be produced daily to maximize the profit?
It is being given that at least one of each must be produced.
By graphical method, the solution of linear programming problem
\[\text{ Subject } to \text{ 3 } x_1 + 2 x_2 \leq 18\]
\[ x_1 \leq 4\]
\[ x_2 \leq 6\]
\[ x_1 \geq 0, x_2 \geq 0, \text{ is } \]
The value of objective function is maximum under linear constraints ______.
Maximum value of 4x + 13y subject to constraints x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0, x + y ≤ 5 and 3x + y ≤ 9 is ______.
The maximum value of Z = 5x + 4y, Subject to y ≤ 2x, x ≤ 2y, x + y ≤ 3, x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0 is ______.
The minimum value of z = 2x + 9y subject to constraints x + y ≥ 1, 2x + 3y ≤ 6, x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0 is ______.
For the function z = 19x + 9y to be maximum under the constraints 2x + 3y ≤ 134, x + 5y ≤ 200, x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0; the values of x and y are ______.
The point which provides the solution to the linear programming problem: Max P = 2x + 3y subject to constraints: x ≥ 0, y ≥ 0, 2x + 2y ≤ 9, 2x + y ≤ 7, x + 2y ≤ 8, is ______
A linear programming problem is given by Z = px + qy where p, q > 0 subject to the constraints: x + y ≤ 60, 5x + y ≤ 100, x ≥ 0 and y ≥ 0
- Solve graphically to find the corner points of the feasible region.
- If Z = px + qy is maximum at (0, 60) and (10, 50), find the relation of p and q. Also mention the number of optimal solution(s) in this case.
