Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
To reduce the resonant frequency in an LCR series circuit with a generator ______.
Options
the generator frequency should be reduced.
another capacitor should be added in parallel to the first.
the iron core of the inductor should be removed.
dielectric in the capacitor should be removed.
Solution
To reduce the resonant frequency in an LCR series circuit with a generator another capacitor should be added in parallel to the first.
Explanation:
At response XL = XC ⇒ ω0L = `1/(ω_0C)`
⇒ ω0 = `1/sqrt(LC) "rad"/sec`
⇒ v0 = `1/(2pisqrt(LC)) Hz`
Resonant frequency in an L-C-R circuit is given by
`v_0 = 1/(2pisqrt(LC))`
If L or C increases, the resonant frequency will reduce.
To increase capacitance, we must connect another capacitor parallel to the first.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A series LCR circuit is connected to an ac source. Using the phasor diagram, derive the expression for the impedance of the circuit. Plot a graph to show the variation of current with frequency of the source, explaining the nature of its variation.
Show that in an a.c. circuit containing a pure inductor, the voltage is ahead of current by π/2 in phase ?
A series LCR circuit is connected to a source having voltage v = vm sin ωt. Derive the expression for the instantaneous current I and its phase relationship to the applied voltage.
Obtain the condition for resonance to occur. Define ‘power factor’. State the conditions under which it is (i) maximum and (ii) minimum.
An inductor of inductance 2.00 H is joined in series with a resistor of resistance 200 Ω and a battery of emf 2.00 V. At t = 10 ms, find (a) the current in the circuit, (b) the power delivered by the battery, (c) the power dissipated in heating the resistor and (d) the rate at which energy is being stored in magnetic field.
A constant current exists in an inductor-coil connected to a battery. The coil is short-circuited and the battery is removed. Show that the charge flown through the coil after the short-circuiting is the same as that which flows in one time constant before the short-circuiting.
(i) An a.c. source of emf ε = 200 sin omegat is connected to a resistor of 50 Ω . calculate :
(1) Average current (`"I"_("avg")`)
(2) Root mean square (rms) value of emf
(ii) State any two characteristics of resonance in an LCR series circuit.
Figure shows a series LCR circuit connected to a variable frequency 230 V source. L = 5.0 H, C = 80 µF, R = 40 Ω.
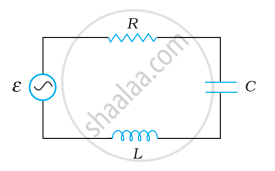
- Determine the source frequency which drives the circuit in resonance.
- Obtain the impedance of the circuit and the amplitude of current at the resonating frequency.
- Determine the rms potential drops across the three elements of the circuit. Show that the potential drop across the LC combination is zero at the resonating frequency.
A series LCR circuit containing 5.0 H inductor, 80 µF capacitor and 40 Ω resistor is connected to 230 V variable frequency ac source. The angular frequencies of the source at which power transferred to the circuit is half the power at the resonant angular frequency are likely to be ______.
As the frequency of an ac circuit increases, the current first increases and then decreases. What combination of circuit elements is most likely to comprise the circuit?
- Inductor and capacitor.
- Resistor and inductor.
- Resistor and capacitor.
- Resistor, inductor and capacitor.
