Advertisements
Advertisements
Questions
Two dice, one blue and one grey, are thrown at the same time.
(i) Write down all the possible outcomes and complete the following table:
| Event : ‘Sum on 2 dice’ |
2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 |
| Probability | `1/36` | `5/36` | `1/36` |
Two dice, one blue and one grey, are thrown at the same time. (i) Complete the following table:
| ‘Sum on 2 dice’ | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 |
| Probability | `1/36` | `5/36` | `1/36` |
(ii) A student argues that there are 11 possible outcomes 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11 and 12. Therefore, each of them has a probability `1/11` Do you agree with this argument? Justify your answer.
Solution
Total no. of possible outcomes when 2 dice are thrown = 6 × 6 = 36 which are
{(1, 1) (1, 2) (1, 3) (1, 4) (1, 5) (1, 6)
(2, 1) (2, 2) (2, 3) (2, 4) (2, 5) (2, 6)
(3, 1) (3, 2) (3, 3) (3, 4) (3, 5) (3, 6)
(4, 1) (4, 2) (4, 3) (4, 4) (4, 5) (4, 6)
(5, 1) (5, 2) (5, 3) (5, 4) (5, 5) (5, 6)
(6, 1) (6, 2) (6, 3) (6, 4) (6, 5) (6, 6)}
E ⟶ event of getting sum on 2 dice as 2
No. of favourable outcomes = 1{(1, 1)}
Probability, P(E) =`"No. of favourable outcomes"/"Total no. of possible outcomes"`
P(E) = `1/36`
E ⟶ event of getting sum as 3
No. of favourable outcomes = 2 {(1, 2) (2, 1)}
P(E) =`2/36`
E ⟶ event of getting sum as 4
No. of favourable outcomes = 3 {(3, 1) (2, 2) (1, 3)}
P(E) =` 3/36`
E ⟶ Event of getting Sum as 5
No. of favourable outcomes = 4 {(1, 4) (2, 3) (3, 2) (4, 1)}
P(E) = `4/36`
E ⟶ event of getting sum as 6
No. of favourable outcomes = 5 {(1, 5) (2, 4) (3, 3) (4, 2) (5, 1)}
P(E) =`5/36`
E ⟶ event of getting sum as 7
No. of favourable outcomes = 6 {(1, 6) (2, 5) (3, 4) (4, 3) (5, 2) (6, 1)}
P(E) =`6/36`
E ⟶ event of getting sum as 8
No. of favourable outcomes = 5 {(2, 6) (3, 5) (4, 4) (5, 3) (6, 2)}
P(E) = `5/36`
E ⟶ Event of getting Sum as 9
No. of favourable outcomes = 4 {(3, 6) (4, 5) (5, 4) (6, 3)}
P(E) = `4/36`
E ⟶ Event of getting Sum as 10
No. of favourable outcomes = 3 {(4, 6) (5, 5) (6, 4)}
P(E) = `3/36`
E ⟶ Event of getting sum as 11.
No. of favourable outcomes = 2 {(5, 6) (6, 5)}
P(E) = `2/36`
E ⟶ Event of getting sum as 12.
No. of favourable Outcomes = 1 {(6, 6)}
P(E) = `1/36`
| ‘Sum on 2 dice’ | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 |
| Probability | `1/36` | `2/36` | `3/36` | `4/36` | `5/36` | `6/36` | `5/36` | `4/36` | `3/36` | `2/36` | `1/36` |
No, the outcomes are not equally likely from the above table. We see that. There is a different Probability for different outcome.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Probability of an event E + Probability of the event ‘not E’ = _______.
The probability of an event that is certain to happen is ______. Such as event is called ______.
Why is tossing a coin considered to be a fair way of deciding which team should get the ball at the beginning of a football game?
Are the arguments in the following sentence correct or not correct? Give a reason for your answer.
If two coins are tossed simultaneously there are three possible outcomes, two heads, two tails or one of each. Therefore, for each of these outcomes, the probability is `1/3.`
Which of the following arguments are correct and which are not correct? Give a reason for your answer.
If a die is thrown, there are two possible outcomes, an odd number or an even number. Therefore, the probability of getting an odd number is 1/2.
A die is thrown once. Find the probability of getting a number lying between 2 and 6.
A die is thrown once. Find the probability of getting an odd number.
In a simultaneous throw of a pair of dice, find the probability of getting an even number on first
One card is drawn from a well-shuffled deck of 52 cards. Find the probability of getting a king of red colour.
A bag contains 5 black, 7 red and 3 white balls. A ball is drawn from the bag at random. Find the probability that the ball drawn is not black
A black die and a white die are thrown at the same time. Write all the possible outcomes. What is the probability that the sum of the numbers appearing on the top of the dice is less than or equal to 12?
One card is drawn from a well shuffled deck of 52 cards. Find the probability of getting a face card
Two customers are visiting a particular shop in the same week (Monday to Saturday). Each is equally likely to visit the shop on any one day as on another. What is the robability that both will visit the shop on the same day?
In a class, there are 18 girls and 16 boys. The class teacher wants to choose one pupil form class monitor. What she does, she writes the name of each pupil on a card and puts them into a basket and mixes thoroughly. A child is asked to pick one card from the basket. What is the probability that the name written on the card is the name of a girl?
What is the probability that a number selected at random from the number 1,2,2,3,3,3, 4, 4, 4, 4 will be their average?
There are 30 cards, of same size, in a bag on which numbers 1 to 30 are written. One card is taken out of the bag at random. Find the probability that the number on the selected card is not divisible by 3.
12 defective pens are accidently mixed with 132 good ones. It is not possible to just look at pen and tell whether or not it is defective. one pen is taken out at random from this lot. Determine the probability that the pen taken out is good one.
Two dice are thrown simultaneously. What is the probability that 5 wifi come up at both dice?
From a well-shuffled deck of 52 playing-cards, one card is drawn. Find the probability that the card drawn will be a black card.
From a well-shuffled deck of 52 playing-cards, one card is drawn. Find the probability that the card drawn will be a face card of red colour.
From a deck of 52 cards, all the face cards are removed and then the remaining cards are shuffled. Now one card is drawn from the remaining deck. Find the probability that the card drawn is a black card.
A bag contains 100 identical marble stones which are numbered 1 to 100. If one stone is drawn at random from the bag, find the probability that it bears a perfect square number.
Two dice (each bearing numbers 1 to 6) are rolled together. Find the probability that the sum of the numbers on the upper-most faces of two dice is between 5 and 8.
From a pack of 52 playing cards, all cards whose numbers are multiples of 3 are removed. A card is now drawn at random. What is the probability that the card drawn is a face card (King, Jack or Queen).
Six faces of a die are as shown below.
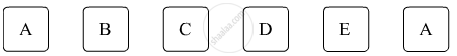
If the die is rolled once, find the probability of -‘D’ appears on upper face.
In a game of chance, a spinning arrow comes to rest at one of the numbers 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8. All these are equally likely outcomes. Find the probability that it will rest at 8.

A bag contains 3 red, 3 white and 3 green balls. One ball is taken out of the bag at random. What is the probability that the ball drawn is –not red.
Tickets numbered 2, 3, 4, 5, ..., 100, 101 are placed in a box and mixed thoroughly. One ticket is drawn at random from the box. Find the probability that the number on the ticket is a number which is a perfect square.
What is the probability of an impossible event?
1000 families with 2 children were selected randomly , and the following data were recorded :
| Number of girls in a family | 0 | 1 | 2 |
| Number of families | 333 | 392 | 275 |
Find the probability of a family , having
(ii) 2 girls
A die is thrown 450 times and frequencies of the outcomes 1,2,3,4,5,6 were noted as given in the following table
| outcomes | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
| Frequency | 73 | 70 | 74 | 75 | 80 | 78 |
(iii) a number > 4
A bag contains 6 black, 7 red, and 2 white balls. A ball is drawn from the bag at random. Find the probability that the ball drawn is black or white.
A letter of English alphabets is chosen at random. What is the probability that it is a letter of the word ‘MATHEMATICS’?
Someone is asked to take a number from 1 to 100. The probability that it is a prime is ______.
Two dice are thrown at the same time. Find the probability of getting same number on both dice.
All the jacks, queens and kings are removed from a deck of 52 playing cards. The remaining cards are well shuffled and then one card is drawn at random. Giving ace a value 1 similar value for other cards, find the probability that the card has a value less than 7
A bag contains 24 balls of which x are red, 2x are white and 3x are blue. A ball is selected at random. What is the probability that it is not red?
An unbiased coin is tossed twice. Find the probability of getting exactly one tail.
