Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Two particles A and B with charges q and 2q, respectively, are placed on a smooth table with a separation d. A third particle C is to be clamped on the table in such a way that the particles A and B remain at rest on the table under electrical forces. What should be the charge on C and where should it be clamped?
Solution
For equilibrium,
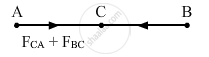
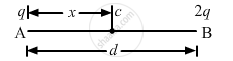
\[\text{Again }, \vec{F}_{AC} = \vec{F}_{CB} \]
\[\text{So} , \frac{1}{x^2} = \frac{2}{\left( d - x \right)^2}\]
\[\text{Or 2 x}^2 = \left( d - x \right)^2 \]
\[ \text{Or }\sqrt{2}x = d - x\]
\[ \text{Or x } = (\sqrt{2} - 1)d\]
For a charge at rest,
\[\vec{F}_{AC} = \vec{F}_{CB} \]
\[\frac{1}{4\pi \in_0}\frac{q\theta}{[(\sqrt{2} - 1)d ]^2} + \frac{1}{4\pi \in_0}\frac{q \times 2q}{d^2}\]
\[ = 0\]
\[ \text{ Or } \theta = (6 - 4\sqrt{2})q\]
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A conducting sphere of radius 10 cm has an unknown charge. If the electric field 20 cm from the centre of the sphere is 1.5 × 103 N/C and points radially inward, what is the net charge on the sphere?
Mark out the correct options.
A point charge is brought inside an electric field. The electric field at a nearby point
(a) will increase if the charge is positive
(b) will decrease if the charge is negative
(c) may increase if the charge is positive
(d) may decrease if the charge is negative
A point charge q is placed in a cavity in a metal block. If a charge Q is brought outside the metal, will the charge q feel an electric fore?
Choose the correct option.
Two point charges of +5 μC are so placed that they experience a force of 8.0 × 10-3N. They are then moved apart so that the force is now 2.0 × 10-3N. The distance between them is now
Electric charge is a property of ______.
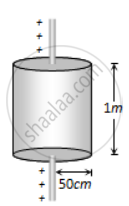
Electric charge is uniformly distributed along a long straight wire of radius 1 mm. The charge per cm length of the wire is Q coulomb. Another cylindrical surface of radius 50 cm and length 1 m symmetrically enclose the wire as shown in the figure. The total electric flux passing through the cylindrical surface is ______.
Equal charge are given to two-sphere of different radii. The potential will be
A metallic spherical shell has an inner radius R1 and outer radius R2. A charge Q is placed at the centre of the spherical cavity. What will be surface charge density on (i) the inner surface, and (ii) the outer surface?
Total charge –Q is uniformly spread along length of a ring of radius R. A small test charge +q of mass m is kept at the centre of the ring and is given a gentle push along the axis of the ring.
- Show that the particle executes a simple harmonic oscillation.
- Obtain its time period.
A certain charge Q is divided into two parts q and (Q - q). How should the charges Q and q be divided so that q and (Q - q) placed at a certain distance apart experience maximum electrostatic repulsion?
A charge of 4 µC is to be divided into two. The distance between the two divided charges is constant. The magnitude of the divided charges so that the force between them is maximum, will be:
A straight infinitely long cylinder of radius R0 = 10 cm is uniformly charged with a surface charge density σ = + 10-12 C/m2. The cylinder serves as a source of electrons, with the velocity of the emitted electrons perpendicular to its surface. Electron velocity must be ______ × 105 m/s to ensure that electrons can move away, from the axis of the cylinder to a distance greater than r = 103 m.
Two particles A and B having the same mass have charges +q and +4q, respectively. When they are allowed to fall from rest through the same electric potential difference the ratio of their speeds vA to vB will become ______.
The potential at a point x (measured in µm) due to some charges situated on the X-axis is given by v(x) = `20/((x^2 - 4)` V. The electric field E at x = 4 µm is given by ______.
