Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Mark out the correct options.
Options
The total charge of the universe is constant.
The total positive charge of the universe is constant.
The total negative charge of the universe is constant.
The total number of charged particles in the universe is constant.
Solution
The total charge of the universe is constant.
According to the principal of conservation of charge, the net amount of positive charge minus the net amount of negative charge in the universe is always constant. Thus, the total charge of the universe is constant. The total positive charge of the universe may increase or decrease, depending on the total increase or decrease in negative charge. This is the principle of conservation of charge that is universal in nature.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A point charge q is placed in a cavity in a metal block. If a charge Q is brought outside the metal, will the charge q feel an electric fore?
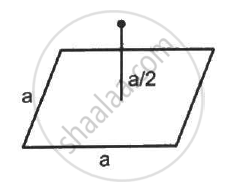
A charge Q is placed at a distance a/2 above the centre of a horizontal, square surface of edge a as shown in the following figure . Find the flux of the electric field through the square surface.
A positive charge Q is distributed uniformly over a circular ring of radius R. A particle of mass m, and a negative charge q, is placed on its axis at a distance x from the centre. Find the force on the particle. Assuming x << R, find the time period of oscillation of the particle if it is released from there .
A rod of length L has a total charge Q distributed uniformly along its length. It is bent in the shape of a semicircle. Find the magnitude of the electric field at the centre of curvature of the semicircle.
A positively charged glass rod is brought close to a metallic rod isolated from ground. The charge on the side of the metallic rod away from the glass rod will be ______.
Two parallel plates have a potential difference of 10 V between them. If the plates are 0.5 mm apart, what will be the strength of electric charge.
Two small spheres 18 cm apart have equal negative charges and repel each other with the force of 6 × 10-3 N. Find the total charge on both spheres.
One metallic sphere A is given a positive charge whereas another identical metallic sphere B of exactly the same mass as A is given an equal amount of negative charge. Then
When 1019 electrons are removed from a neutral metal plate through some process, the electric charge on it is ______
A conducting sphere of radius 0.104 m has an unknown charge. If the electric field at 0.20 m from the centre of the sphere is 1.5 x 103 NC-1 and points radially inward, what is the electric flux?
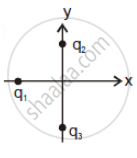
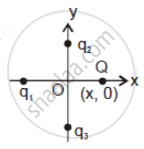
In figure two positive charges q2 and q3 fixed along the y-axis, exert a net electric force in the + x-direction on a charge q1 fixed along the x-axis. If a positive charge Q is added at (x, 0), the force on q1 ______.
(1) |
(2) |
A solid sphere of radius R1 and volume charge density `rho = rho_0/"r"` is enclosed by a hollow sphere of radius R2 with negative surface charge density σ, such that the total charge in the system is zero. `rho_0` is a positive constant and r is the distance from the center of the sphere. The ratio R2/R1 is ______.
Two charges q1 and q2 are placed in vacuum at a distance d and the force acting between them is F. If a medium of dielectric constant 4 is introduced around them, the force now will be ______.
Equal charge are given to two-sphere of different radii. The potential will be
Total charge –Q is uniformly spread along length of a ring of radius R. A small test charge +q of mass m is kept at the centre of the ring and is given a gentle push along the axis of the ring.
- Show that the particle executes a simple harmonic oscillation.
- Obtain its time period.
Given below are two statements:
- Statement I: The electric force changes the speed of the charged particle and hence changes its kinetic energy; whereas the magnetic force does not change the kinetic energy of the charged particle.
- Statement II: The electric force accelerates the positively charged particle perpendicular to the direction of the electric field. The magnetic force accelerates the moving charged particle along the direction of the magnetic field.
In light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below.
A straight infinitely long cylinder of radius R0 = 10 cm is uniformly charged with a surface charge density σ = + 10-12 C/m2. The cylinder serves as a source of electrons, with the velocity of the emitted electrons perpendicular to its surface. Electron velocity must be ______ × 105 m/s to ensure that electrons can move away, from the axis of the cylinder to a distance greater than r = 103 m.
Two particles A and B having the same mass have charges +q and +4q, respectively. When they are allowed to fall from rest through the same electric potential difference the ratio of their speeds vA to vB will become ______.
