Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A positive charge Q is distributed uniformly over a circular ring of radius R. A particle of mass m, and a negative charge q, is placed on its axis at a distance x from the centre. Find the force on the particle. Assuming x << R, find the time period of oscillation of the particle if it is released from there .
Solution
Consider an element of angular width \[d\theta\] at a distance r from the charge q on the circular ring, as shown in the figure.
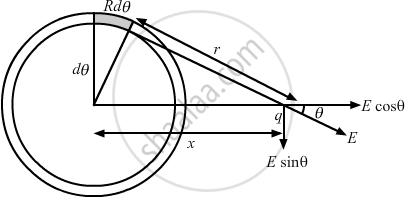
\[dE = \frac{dq}{4\pi \epsilon_0}\frac{1}{r^2}\]
\[ = \frac{\frac{Q}{2\pi}d\theta}{4\pi \epsilon_0}\frac{1}{R^2 + x^2}\]
By the symmetry, the E sinθ component of all such elements on the ring will vanish.
So, net electric field,
\[d E_{net} = dE\cos\theta = \frac{Qd\theta}{8 \pi^2 \epsilon_0 \left( R^2 + x^2 \right)^{3/2}}\]
Total force on the charged particle,
\[F = \int qd E_{net} \]
\[ = \frac{qQ}{8 \pi^2 \epsilon_0}\frac{x}{\left( R^2 + x^2 \right)^{3/2}} \int_0^{2\pi} d\theta\]
\[ = \frac{xQq}{4\pi \epsilon_0 \left( R^2 + x^2 \right)^{3/2}}\]
According to the question,
\[x < < R\]
\[F = \frac{Qq x}{4\pi \epsilon_0 R^3}\]
Comparing this with the condition of simple harmonic motion, we get
\[F = m \omega^2 x\]
\[ \Rightarrow m \omega^2 = \frac{Qq}{4\pi \epsilon_0 R^3}\]
\[ \Rightarrow m \left( \frac{2\pi}{T} \right)^2 = \frac{Qq}{4\pi \epsilon_0 R^3}\]
\[ \Rightarrow T = \left[ \frac{16 \pi^3 \epsilon_0 m R^3}{Qq} \right]^{1/2}\]
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A conducting sphere of radius 10 cm has an unknown charge. If the electric field 20 cm from the centre of the sphere is 1.5 × 103 N/C and points radially inward, what is the net charge on the sphere?
A proton and an electron are placed in a uniform electric field.
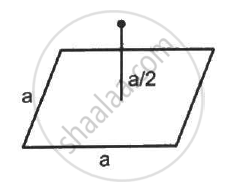
A charge Q is placed at a distance a/2 above the centre of a horizontal, square surface of edge a as shown in the following figure . Find the flux of the electric field through the square surface.
Two large conducting plates are placed parallel to each other with a separation of 2⋅00 cm between them. An electron starting from rest near one of the plates reaches the other plate in 2⋅00 microseconds. Find the surface charge density on the inner surfaces.
A positive charge q is placed in front of a conducting solid cube at a distance d from its centre. Find the electric field at the centre of the cube to the charges appearing on its surface.
A positively charged glass rod is brought close to a metallic rod isolated from ground. The charge on the side of the metallic rod away from the glass rod will be ______.
Two parallel plates have a potential difference of 10 V between them. If the plates are 0.5 mm apart, what will be the strength of electric charge.
Two small conducting spheres of equal radius have charges +10 µC and -20 µC respectively and placed at a distance R from each other experience force F1· If they are brought in contact and separated to the same distance, they experience force F2. The ratio of F1 to F2 is ____________.
A conducting sphere of radius 0.104 m has an unknown charge. If the electric field at 0.20 m from the centre of the sphere is 1.5 x 103 NC-1 and points radially inward, what is the electric flux?
A solid sphere of radius R1 and volume charge density `rho = rho_0/"r"` is enclosed by a hollow sphere of radius R2 with negative surface charge density σ, such that the total charge in the system is zero. `rho_0` is a positive constant and r is the distance from the center of the sphere. The ratio R2/R1 is ______.
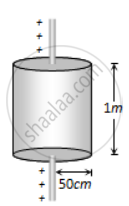
Electric charge is uniformly distributed along a long straight wire of radius 1 mm. The charge per cm length of the wire is Q coulomb. Another cylindrical surface of radius 50 cm and length 1 m symmetrically enclose the wire as shown in the figure. The total electric flux passing through the cylindrical surface is ______.
Electric field lines provide information about ______.
Two charges q1 and q2 are placed in vacuum at a distance d and the force acting between them is F. If a medium of dielectric constant 4 is introduced around them, the force now will be ______.
Which one of the following is the unit of electric charge?
Given below are two statements:
- Statement I: The electric force changes the speed of the charged particle and hence changes its kinetic energy; whereas the magnetic force does not change the kinetic energy of the charged particle.
- Statement II: The electric force accelerates the positively charged particle perpendicular to the direction of the electric field. The magnetic force accelerates the moving charged particle along the direction of the magnetic field.
In light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below.
Two identical metallic spheres A and B when placed at certain distance in air repel each other with a force of F. Another identical uncharged sphere C is first placed in contact with A and then in contact with B and finally placed at midpoint between spheres A and B. The force experienced by sphere C will be:
