Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Two small spheres, each with a mass of 20 g, are suspended from a common point by two insulating strings of length 40 cm each. The spheres are identically charged and the separation between the balls at equilibrium is found to be 4 cm. Find the charge on each sphere.
Solution
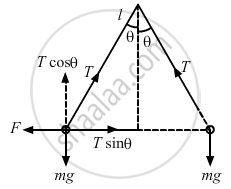
Tcosθ = mg ...(i)
Tsinθ = Fe ...(ii)
Here,
\[F_e = \frac{1}{4 \pi\epsilon_0}\frac{q^2}{r^2}\]
\[\tan\theta = \frac{2}{39 . 9}\]
Dividing equation (ii) by (i), we get
\[\tan\theta = \frac{F_e}{\text{ mg }}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \tan\theta = \frac{1}{4 \pi\epsilon_0}\frac{q^2}{r^2} . \frac{1}{\text{mg}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow q^2 = \frac{\tan\theta . r^2 . \text{mg}}{1/4 \pi\epsilon_0}\]
\[ \Rightarrow q^2 = 17 \times {10}^{- 16} \]
\[ \Rightarrow q = 4 . 123 \times {10}^{- 8} C\]
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A particle of mass m and charge (−q) enters the region between the two charged plates initially moving along x-axis with speed vx (like particle 1 in the fig.). The length of plate is L and an uniform electric field E is maintained between the plates. Show that the vertical deflection of the particle at the far edge of the plate is qEL2/(2m`"v"_"x"^2`).

Four charges +q, −q, +q and −q are to be arranged respectively at the four corners of a square ABCD of side 'a'.
(a) Find the work required to put together this arrangement.
(b) A charge q0 is brought to the centre of the square, the four charges being held fixed. How much extra work is needed to do this ?
Write any two important points of similarities and differences each between Coulomb's law for the electrostatic field and Biot-Savart's law of the magnetic field ?
A charge of 1.0 C is placed at the top of your college building and another equal charge at the top of your house. Take the separation between the two charges to be 2.0 km. Find the force exerted by the charges on each other. How many times your weight is this force?
One end of a 10 cm long silk thread is fixed to a large vertical surface of a charged non-conducting plate and the other end is fastened to a small ball of mass 10 g and a charge of 4.0× 10-6 C. In equilibrium, the thread makes an angle of 60° with the vertical. Find the surface charge density on the plate.
Ten positively-charged particles are kept fixed on the x-axis at points x = 10 cm, 20 cm, 30 cm, ...., 100 cm. the first particle has a charge 1.0 × 10−8 C, the second 8 × 10−8 C, the third 27 × 10−8 C and so on. The tenth particle has a charge 1000 × 10−8 C. Find the magnitude of the electric force acting on a 1 C charge placed at the origin.
Two identical balls, each with a charge of 2.00 × 10−7 C and a mass of 100 g, are suspended from a common point by two insulating strings, each 50 cm long. The balls are held at a separation 5.0 cm apart and then released. Find.
(a) the electric force on one of the charged balls
(b) the components of the resultant force on it along and perpendicular to the string
(c) the tension in the string
(d) the acceleration of one of the balls. Answers are to be obtained only for the instant just after the release.
A particle A with a charge of 2.0 × 10−6 C is held fixed on a horizontal table. A second charged particle of mass 80 g stays in equilibrium on the table at a distance of 10 cm from the first charge. The coefficient of friction between the table and this second particle is μ = 0.2. Find the range within which the charge of this second particle may lie.
A particle A with a charge of 2.0 × 10−6 C and a mass of 100 g is placed at the bottom of a smooth inclined plane of inclination 30°. Where should another particle B, with the same charge and mass, be placed on the incline so that it may remain in equilibrium?
Two particles A and B, each carrying a charge Q, are held fixed with a separation dbetween them. A particle C of mass m and charge q is kept at the middle point of the line AB. Assuming x<<d, show that this force is proportional to x.
Three identical charges, each with a value of 1.0 × 10−8 C, are placed at the corners of an equilateral triangle of side 20 cm. Find the electric field and potential at the centre of the triangle.
Three charges +Q, q, +Q are placed respectively, at distance, 0, d/2 and d from the origin, on the X-axis. If the net force experienced by +Q, placed at x = 0, is zero then value of q is ____________.
Two charges of equal magnitudes kept at a distance r exert a force F on each other. If the charges are halved and distance between them is doubled, then the new force acting on each charge is ______.
According to Coulomb's law, which is the correct relation for the following figure?

Which of the following statements about nuclear forces is not true?
Two point charges Q each are placed at a distance d apart. A third point charge q is placed at a distance x from the mid-point on the perpendicular bisector. The value of x at which charge q will experience the maximum Coulomb's force is ______.
Four charges equal to −Q are placed at the four a corners of a square and charge q is at its centre. If the system is in equilibrium, the value of q is ______.
