Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
One end of a 10 cm long silk thread is fixed to a large vertical surface of a charged non-conducting plate and the other end is fastened to a small ball of mass 10 g and a charge of 4.0× 10-6 C. In equilibrium, the thread makes an angle of 60° with the vertical. Find the surface charge density on the plate.
Solution
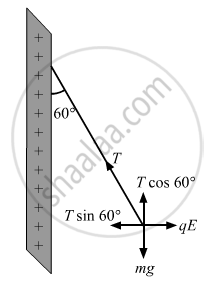
There are two forces acting on the ball. These are
(1) Weight of the ball, W = mg
(2) Coulomb force acting on the charged ball due to the electric field of the plate, F = qE
Due to these forces,a tension develops in the thread.
Let the surface charge density on the plate be σ.
Electric field of a plate,
`"E" = sigma /(2∈_0)`
It is given that in equilibrium, the thread makes an angle of 60° with the vertical.
Resolving the tension in the string along horizontal and vertical directions, we get:
T cos 60° = mg
T sin 60° = qE
`=> tan 60° = "qE"/"mg"`
`=> "E" = ("mg" tan 60 °)/q`
Also, electric field due to a plate,
`"E" = sigma/ 2 ∈_0 =( "mg" tan 60°)/q`
`sigma =(2 ∈_0 "mg" tan 60 °)/"q"`
`sigma =( 2 xx (8.55 xx 10^-12 ) xx ( 10 xx 10 ^-3 xx 9.8) xx 1.7320)/(4.0 xx 10^-6)`
σ = 7.5× 10-7 C/m2
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Check that the ratio ke2/G memp is dimensionless. Look up a Table of Physical Constants and determine the value of this ratio. What does the ratio signify?
Three-point charges q, – 4q and 2q are placed at the vertices of an equilateral triangle ABC of side 'l' as shown in the figure. Obtain the expression for the magnitude of the resultant electric force acting on the charge q

(b) Find out the amount of the work done to separate the charges at infinite distance.
Does the force on a charge due to another charge depend on the charges present nearby?
Three equal charges, 2.0 × 10−6 C each, are held at the three corners of an equilateral triangle of side 5 cm. Find the Coulomb force experienced by one of the charges due to the other two.
Four equal charges of 2.0 × 10−6 C each are fixed at the four corners of a square of side 5 cm. Find the Coulomb's force experienced by one of the charges due to the other three.
Ten positively-charged particles are kept fixed on the x-axis at points x = 10 cm, 20 cm, 30 cm, ...., 100 cm. the first particle has a charge 1.0 × 10−8 C, the second 8 × 10−8 C, the third 27 × 10−8 C and so on. The tenth particle has a charge 1000 × 10−8 C. Find the magnitude of the electric force acting on a 1 C charge placed at the origin.
Two charged particles with charge 2.0 × 10−8 C each are joined by an insulating string of length 1 m and the system is kept on a smooth horizontal table. Find the tension in the string.
Two identical pith balls are charged by rubbing one against the other. They are suspended from a horizontal rod through two strings of length 20 cm each, the separation between the suspension points being 5 cm. In equilibrium, the separation between the balls is 3 cm. Find the mass of each ball and the tension in the strings. The charge on each ball has a magnitude 2.0 × 10−8 C.
Two small spheres, each with a mass of 20 g, are suspended from a common point by two insulating strings of length 40 cm each. The spheres are identically charged and the separation between the balls at equilibrium is found to be 4 cm. Find the charge on each sphere.
A water particle of mass 10.0 mg and with a charge of 1.50 × 10−6 C stays suspended in a room. What is the magnitude of electric field in the room? What is its direction ?
Three identical charges, each with a value of 1.0 × 10−8 C, are placed at the corners of an equilateral triangle of side 20 cm. Find the electric field and potential at the centre of the triangle.
A total charge Q is broken in two parts Q1 and Q2 and they are placed at a distance R from each other. The maximum force of repulsion between them will occur, when ____________.
Two point charges +3 µC and +8 µC repel each other with a force of 40 N. If a charge of -5 µC is added to each of them, then force between them will become ______.
Two positive charges ______.
For charges q1 and q2 separated by a distance R the magnitude of the electrostatic force is given by ______.
The unit of charge is ______.
A charge Q is divided into two parts of q and Q – q. If the coulomb repulsion between them when they are separated is to be maximum, the ratio of Q/q should be ______.
Coulomb's law is given by F = k q1q2 rn where n is
