Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A charged particle with a charge of −2⋅0 × 10−6 C is placed close to a non-conducting plate with a surface charge density of 4.0 × 10-6Cm0-2. Find the force of attraction between the particle and the plate.
Solution
The electric field due to a conducting thin sheet,
`"E" = sigma/( 2 ∈ _0)`
The magnitude of attractive force between the particle and the plate,
F =qE
`"F" = (q xx sigma)/(2∈_0)`
`"F" = ((2.0 xx 10^-6 ) xx ( 4.0 xx 10^-6))/(2 xx (8.55 xx 10^-12))`
F = 0.45 N
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
plot a graph showing the variation of current density (j) versus the electric field (E) for two conductors of different materials. What information from this plot regarding the properties of the conducting material, can be obtained which can be used to select suitable materials for use in making (i) standard resistance and (ii) connecting wires in electric circuits?
Why is the potential inside a hollow spherical charged conductor constant and has the same value of as on its surface?
A metallic particle with no net charge is placed near a finite metal plate carrying a positive charge. The electric force on the particle will be
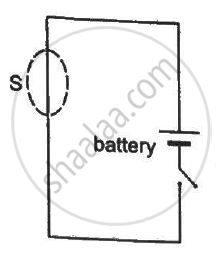
A closed surface S is constructed around a conducting wire connected to a battery and a switch in the following figure. As the switch is closed, the free electrons in the wire start moving along the wire. In any time interval, the number of electrons entering the closed surface S is equal to the number of electrons leaving it. On closing the switch, the flux of the electric field through the closed surface
(a) is increased
(b) is decreased
(c) remains unchanged
(d) remains zero
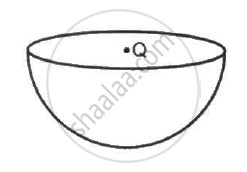
A charge Q is placed at the centre of an imaginary hemispherical surface. Using symmetry arguments and Gauss's Law, find the flux of the electric field due to this charge through the surface of the hemisphere in the following figure.
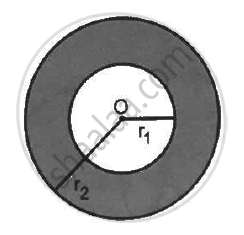
A charge Q is distributed uniformly within the material of a hollow sphere of inner and outer radii r1 and r2 (see the figure). Find the electric field at a point P at a distance x away from the centre for r1 < x < r. Draw a rough graph showing the electric field as a function of x for 0 < x < 2r2 (see the figure).
A charge Q is placed at the centre of an uncharged, hollow metallic sphere of radius a. (a) Find the surface. (b) If a charge q is put on the sphere, what would be the surface charge densities on the inner and outer surfaces? (c) Find the electric field inside the sphere at a distance x from the centre in the situations (a) and (b).
Consider the following very rough model of a beryllium atom. The nucleus has four protons and four neutrons confined to a small volume of radius 10−15 m. The two 1 selectrons make a spherical charge cloud at an average distance of 1⋅3 ×10−11 m from the nucleus, whereas the two 2 s electrons make another spherical cloud at an average distance of 5⋅2 × 10−11 m from the nucleus. Find three electric fields at (a) a point just inside the 1 s cloud and (b) a point just inside the 2 s cloud.
Find the magnitude of the electric field at a point 4 cm away from a line charge of density 2 × 10-6 Cm-1.
A long cylindrical wire carries a positive charge of linear density 2.0 × 10-8 C m -1 An electron revolves around it in a circular path under the influence of the attractive electrostatic force. Find the kinetic energy of the electron. Note that it is independent of the radius.
One end of a 10 cm long silk thread is fixed to a large vertical surface of a charged non-conducting plate and the other end is fastened to a small ball of mass 10 g and a charge of 4.0× 10-6 C. In equilibrium, the thread makes an angle of 60° with the vertical (a) Find the tension in the string in equilibrium. (b) Suppose the ball is slightly pushed aside and released. Find the time period of the small oscillations.
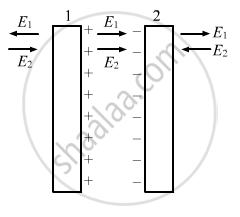
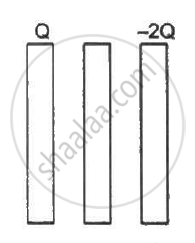
Three identical metal plates with large surface areas are kept parallel to each other as shown in the following figure. The leftmost plate is given a charge Q, the rightmost a charge −2Q and the middle one is kept neutral. Find the charge appearing on the outer surface of the rightmost plate.
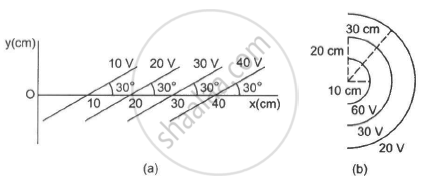
Some equipotential surface is shown in the figure. What can you say about the magnitude and the direction of the electric field?
Draw equipotential surfaces corresponding to a uniform electric field in the z-directions.
Pick out the statement which is incorrect
