Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
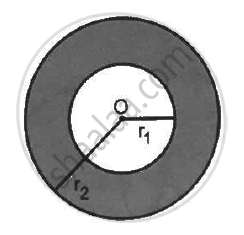
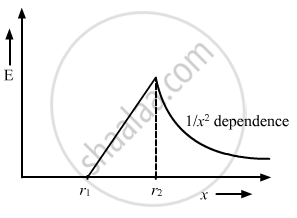
A charge Q is distributed uniformly within the material of a hollow sphere of inner and outer radii r1 and r2 (see the figure). Find the electric field at a point P at a distance x away from the centre for r1 < x < r. Draw a rough graph showing the electric field as a function of x for 0 < x < 2r2 (see the figure).
Solution
Amount of charge present on the hollow sphere = Q
Inner radii of the hollow sphere = r1
Outer radii of the hollow sphere = r2
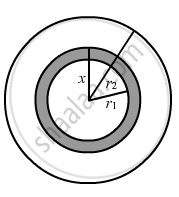
Consider an imaginary sphere of radius x.
The charge on the sphere can be found by multiplying the volume charge density of the hollow spherical volume with the volume of the imaginary sphere of radius (x-r1).
Charge per unit volume of the hollow sphere,
`ρ = "Q"/( 4/3pi("r"_2^3 -"r"_1^3))`
Charge enclosed by this imaginary sphere of radius x:-
q = ρ × Volume of the part consisting of charge
`"q" = (4/3 pi ("x"^3 -"r"_1^3)"Q")/(4/3pi ("r"_2^3))`
`"q" = (("x"^3 -"r"_1^3))/(("r"_2^3 - "r"_1^3)) "Q"`
According to Gauss's Law,
`oint "E" . "d""s" = "q"/∈_0`
Here, the surface integral is carried out on the sphere of radius x and q is the charge enclosed by this sphere.
`"E" oint "d""s" = "q"/∈_0`
`"E" (4 pi "x"^2) = "q"/∈_0`
` "E" (4 pi "x"^2) = (("x"^3 -"r"_1^3)"Q")/((("r"_2^3 -"r"_1^3)) ∈_0)`
`"E" =("Q"("x"^3 - "r"_1^3))/( 4pi ∈_0 "x"^2 ("r"_2^3 - "r"_1^3)) `
The electric field is directly proportional to x for r1 < x < r.
The electric field for r2 < x < 2r2,
`"E" = "Q" / (4 pi ∈_0 "x"^2) `
Thus, the graph can be drawn as:-
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
(i) If two similar large plates, each of area A having surface charge densities +σ and –σ are separated by a distance d in air, find the expressions for
(a) field at points between the two plates and on outer side of the plates. Specify the direction of the field in each case.
(b) the potential difference between the plates.
(c) the capacitance of the capacitor so formed.
(ii) Two metallic spheres of Radii R and 2R are charged so that both of these have same surface charge density σ. If they are connected to each other with a conducting wire, inn which direction will the charge flow and why?
Why is the potential inside a hollow spherical charged conductor constant and has the same value of as on its surface?
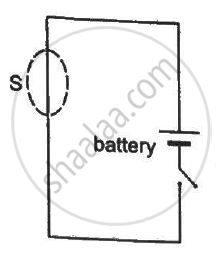
A closed surface S is constructed around a conducting wire connected to a battery and a switch in the following figure. As the switch is closed, the free electrons in the wire start moving along the wire. In any time interval, the number of electrons entering the closed surface S is equal to the number of electrons leaving it. On closing the switch, the flux of the electric field through the closed surface
(a) is increased
(b) is decreased
(c) remains unchanged
(d) remains zero
Show that there can be no net charge in a region in which the electric field is uniform at all points.
The electric field in a region is given by
`vec"E"= 3/5"E"_0 vec"i" + 4/5 "E"_0 vec "i" "with" " E"_0 = 2.0 xx 10^3 "N""C"^-1.`
Find the flux of this field through a rectangular surface of area 0⋅2 m2 parallel to the y-z plane.
A charge Q is placed at the centre of an uncharged, hollow metallic sphere of radius a. (a) Find the surface. (b) If a charge q is put on the sphere, what would be the surface charge densities on the inner and outer surfaces? (c) Find the electric field inside the sphere at a distance x from the centre in the situations (a) and (b).
Find the magnitude of the electric field at a point 4 cm away from a line charge of density 2 × 10-6 Cm-1.
A charged particle with a charge of −2⋅0 × 10−6 C is placed close to a non-conducting plate with a surface charge density of 4.0 × 10-6Cm0-2. Find the force of attraction between the particle and the plate.
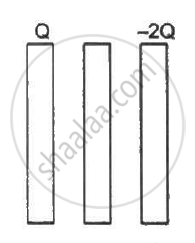
Three identical metal plates with large surface areas are kept parallel to each other as shown in the following figure. The leftmost plate is given a charge Q, the rightmost a charge −2Q and the middle one is kept neutral. Find the charge appearing on the outer surface of the rightmost plate.
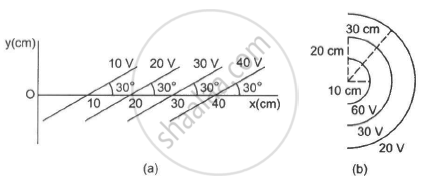
Some equipotential surface is shown in the figure. What can you say about the magnitude and the direction of the electric field?
Consider a circular ring of radius r, uniformly charged with linear charge density λ. Find the electric potential at a point on the axis at a distance x from the centre of the ring. Using this expression for the potential, find the electric field at this point.
A uniform field of 2.0 NC−1 exists in space in the x-direction. (a) Taking the potential at the origin to be zero, write an expression for the potential at a general point (x, y, z). (b) At which point, the potential is 25 V? (c) If the potential at the origin is taken to be 100 V, what will be the expression for the potential at a general point? (d) What will be the potential at the origin if the potential at infinity is taken to be zero? Is it practical to choose the potential at infinity to be zero?
Draw equipotential surfaces corresponding to a uniform electric field in the z-directions.
A simple pendulum consists of a small sphere of mass m suspended by a thread of length l. The sphere carries a positive charge q. The pendulum is placed in a uniform electric field of strength E directed vertically downwards. Find the period of oscillation of the pendulum due to the electrostatic force acting on the sphere, neglecting the effect of the gravitational force.
When a comb rubbed with dry hair attracts pieces of paper. This is because the ______.
A charge Q is applied to a conducting sphere of radius R. At the sphere's centre, the electric potential and electric field are respectively
Pick out the statement which is incorrect
Two charged conducting spheres of radii a and b are connected to each other by a wire. Find the ratio of the electric fields at their surfaces.
