Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Using ruler and compasses only,
- Construct triangle ABC, having given BC = 7 cm, AB – AC = 1 cm and ∠ABC = 45°.
- Inscribe a circle in the ΔABC constructed in (i) above. Measure its radius.
Solution
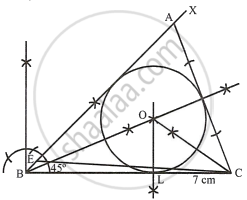
Steps of construction:
i. Construction of triangle:
a. Draw a line segment BC = 7 cm.
b. At B, draw a ray BX making an angle of 45° and cut off BE = AB − AC = 1 cm.
c. Join EC and draw the perpendicular bisector of EC intersecting BX at A.
d. Join AC.
ΔABC is the required triangle.
ii. Construction of incircle:
e. Draw angle bisectors of ∠ABC and ∠ACB intersecting each other at O.
f. From O, draw perpendiculars OL to BC.
g. O as centre and OL as radius draw circle which touches the sides of the ΔABC.
This is the required in-circle of ΔABC.
On measuring, radius OL = 1.8 cm.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Construct a regular hexagon of side 5 cm. Hence construct all its lines of symmetry and name them.
Using ruler and compasses only, draw an equilateral triangle of side 5 cm. Draw its inscribed circle. Measure the radius of the circle.
Using ruler and compasses only,
- Construct a triangle ABC with the following data :
Base AB = 6 cm, BC = 6.2 cm and ∠CAB = 60°. - In the same diagram, draw a circle which passes through the points A, B and C and mark its center O.
- Draw a perpendicular from O to AB which meets AB in D.
- Prove that : AD = BD.
Perpendicular bisectors of the sides AB and AC of a triangle ABC meet at O.
- What do you call the point O?
- What is the relation between the distances OA, OB and OC?
- Does the perpendicular bisector of BC pass through O?
Constuct a triangle ABC with AB = 5.5 cm, AC = 6 cm and ∠BAC = 105°. Hence:
- Construct the locus of point equdistant from BA and BC.
- Construct the locus of points equidistant from B and C.
- Mark the point which satisfies the above two loci as P. Measure and write the length of PC.
Using ruler and compasses only, construct a triangle ABC in which AB=S cm, BC=6 cm and CA=4.5 cm. Construct a circle passing through A, Band c.
Draw a circle with radius 3 cm and inscribe an equilateral triangle in it.
Draw a circle of radius 2. 5 cm and circumscribe a square about it.
Construct an isosceles triangle ABC such that AB = 6 cm, BC = AC = 4 cm. Bisect ∠C internally and mark a point P on this bisector such that CP = 5 cm. Find the points Q and R which are 5 cm from P and also 5 cm from the line AB.
Construct a triangle whose sides are 4.4 cm, 5.2 cm, and 7.1 cm. Construct its circumcircle. Write also the steps of construction.
