Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Which of the following statements are correct about the kinetics of this reaction?
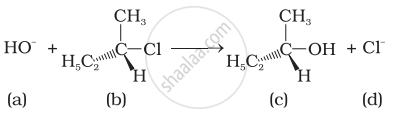
(i) The rate of reaction depends on the concentration of only (b).
(ii) The rate of reaction depends on concentration of both (a) and (b).
(iii) Molecularity of reaction is one.
(iv) Molecularity of reaction is two.
Solution
(i) The rate of reaction depends on the concentration of only (b).
(iii) Molecularity of reaction is one.
Explanation:
SN1 occurs in two steps. I, the polarized \[\ce{C - Cl}\] bond undergoes slow cleavage to produce a carbonation and a chloride ion. The carbocation thus formed is then attacked by nucleophile in step II to complete the substitution reaction. Step I is the slowest and reversible. It involves the \[\ce{C - Cl}\] bond breaking for which the energy is obtained through salvation of halide ion with the proton of protic solvent. Since the rate of reaction depends upon the slowest step, the rate of reaction depends only on the concentration of alkyl halide and not on the concentration of hydroxide ion. So, the rate-determining step is unimolecular.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
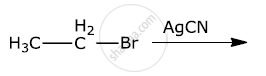
Write the major products(s) in the following:
In the following pair of halogen compounds, which compound undergoes a faster SN1 reaction?
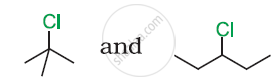
What are ambident nucleophiles? Explain with an example.
Which compound in the following pair will react faster in SN2 reaction with OH−?
CH3Br or CH3I
Given reasons: The dipole moment of chlorobenzene is lower than that of cyclohexyl chloride.
Given reasons: SN1 reactions are accompanied by racemization in optically active alkyl halides.
Which of the following is optically inactive?
In the SN1 reaction, racemization takes place. It is due to:
Why are aryl halides less reactive towards nucleophilic substitution reactions than alkyl halides? How can we enhance the reactivity of aryl halides?
Explain why Grignard reagents should be prepared under anhydrous conditions.
