Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Which of the following statements are not correct?
(i) \[\ce{NaCl}\] being an ionic compound is a good conductor of electricity in the solid state.
(ii) In canonical structures there is a difference in the arrangement of atoms.
(iii) Hybrid orbitals form stronger bonds than pure orbitals.
(iv) \[\ce{VSEPR}\] Theory can explain the square planar geometry of \[\ce{XeF4}\].
Solution
(i) \[\ce{NaCl}\] being an ionic compound is a good conductor of electricity in the solid state.
(ii) In canonical structures there is a difference in the arrangement of atoms.
Explanation:
(i) \[\ce{NaCl}\] being an ionic compound is a good conductor of electricity in the molten state. It is not a bad conductor of electricity in solid-state. So, the statement mentioned in the question is not correct. Hence, this is the correct answer.
(ii) There is no difference in the arrangement of atoms in the canonical structures. The difference is in the arrangement of electron pairs in the canonical structures. So, the statement mentioned in the question is not correct. Hence, this is the correct answer.
(iii) The hybrid orbitals have the same energy and shape and hence they are more effective in the formation of stable bonds than the pure atomic orbitals. So, the statement given is correct. Hence, this is not the correct answer.
(iv) \[\ce{XeF4}\] acquires a square planar geometry, this can very well be explained by the \[\ce{VSEPR}\] theory. The hybridisation of the central xenon atom will be sp3d2 due to the presence of two lone pairs of electrons on the central xenon atom. So, the statement given is correct. Hence, this is not the correct answer.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Explain the important aspects of resonance with reference to the `"CO"_3^(2-)` ion.
H3PO3 can be represented by structures 1 and 2 shown below. Can these two structures be taken as the canonical forms of the resonance hybrid representing H3PO3? If not, give reasons for the same.
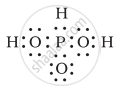 |
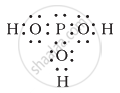 |
| (1) | (2) |
Write the resonance structure for SO3.
Write the resonance structures for NO2.
Write the resonance structures for `"NO"_3^(-)`.
Which of the following species has tetrahedral geometry?
Explain why \[\ce{CO^{2–}3}\] ion cannot be represented by a single Lewis structure. How can it be best represented?
Draw the resonating structure of ozone molecule
Resonance structures can be written for ______.
The acceptable resonating structures of the following molecule are:
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{CH3 - CH = C - \overset{\bullet\bullet}{\underset{\bullet\bullet}{O}} - CH2 - CH3}\\
|\phantom{......}\\
\ce{:N}\phantom{.......}\\
\phantom{}/\phantom{...}\backslash\phantom{......}\\
\phantom{}\ce{H3C}\phantom{.....}\ce{CH3}\phantom{......}
\end{array}\]
| (x) | \[\begin{array}{cc} \ce{CH3 - \overset{\overset{Θ}{\bullet\bullet}}{C}H - C - \overset{\bullet\bullet}{\underset{\bullet\bullet}{O}} - CH2 - CH3}\\ ||\phantom{......}\\ \ce{N^⊕}\phantom{.....}\\ \phantom{}/\phantom{...}\backslash\phantom{......}\\ \phantom{}\ce{H3C}\phantom{.....}\ce{CH3}\phantom{......} \end{array}\] |
| (y) | \[\begin{array}{cc} \ce{CH3 - \overset{\overset{Θ}{\bullet\bullet}}{C}H - C = \overset{⊕}{\underset{\bullet\bullet}{O}} - CH2 - CH3}\\ |\phantom{......}\\ \ce{:N}\phantom{.......}\\ \phantom{}/\phantom{...}\backslash\phantom{......}\\ \phantom{}\ce{H3C}\phantom{.....}\ce{CH3}\phantom{......} \end{array}\] |
| (z) | \[\begin{array}{cc} \ce{CH3 - \overset{⊕}{C}H - C - \overset{\bullet\bullet}{\underset{\bullet\bullet}{O}} - CH2 - CH3}\\ ||\phantom{......}\\ \ce{N^Θ}\phantom{.....}\\ \phantom{}/\phantom{...}\backslash\phantom{......}\\ \phantom{}\ce{H3C}\phantom{.....}\ce{CH3}\phantom{......} \end{array}\] |
| (w) | \[\begin{array}{cc} \ce{CH3 - \overset{⊕}{C}H - C = \overset{Θ}{O} - CH2 - CH3}\\ |\phantom{......}\\ \ce{:N}\phantom{.......}\\ \phantom{}/\phantom{...}\backslash\phantom{......}\\ \phantom{}\ce{H3C}\phantom{.....}\ce{CH3}\phantom{......} \end{array}\] |
