Advertisements
Advertisements
Questions
Which one of the following particles cannot be accelerated by a cyclotron?
(A) Electrons
(B) Protons
(C) Deuterons
(D) α- particles
Which one of the following particles cannot be accelerated by a cyclotron?
(A) Protons
(B) Neutrons
(C) α-particles
(D) Deuterons
Solution
A cyclotron cannot acceletate the following particles
Electrons
Neutrons
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Draw a neat labelled diagram for the construction of 'cyclotron'
In a cyclotron, magnetic field of 3·5Wb/m2 is used to accelerate protons. What should be the time interval in which the electric field between the Dees be reversed?
(Mass of proton = 1· 67 x 10-27Kg, Charge on proton =1·6x10-19c).
State the principle of a cyclotron.
Show that the time period of revolution of particles in a cyclotron is independent of their speeds. Why is this property necessary for the operation of a cyclotron?
Deduce an expression for the frequency of revolution of a charged particle in a magnetic field and show that it is independent of velocity or energy of the particle.
If a watch-glass containing a small quantity of water is placed on two dissimilar magnetic poles, then water ______.
Obtain the expression for the cyclotron frequency.
A deuteron and a proton are accelerated by the cyclotron. Can both be accelerated with the same oscillator frequency? Give reason to justify your answer.
Explain the principle and working of a cyclotron with the help of a schematic diagram. Write the expression for cyclotron frequency.
Verify that the units weber and volt second are the same.
Which of the following particles will describe the smallest circle when projected with the same velocity perpendicular to a magnetic field?
Consider a 10-cm long portion of a straight wire carrying a current of 10 A placed in a magnetic field of 0.1 T making an angle of 53° with the wire. What magnetic force does the wire experience?
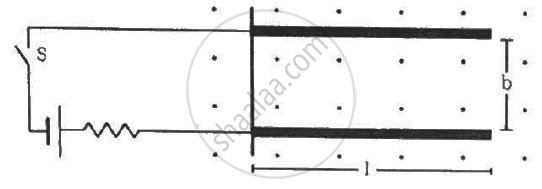
Two metal strips, each of length l, are clamped parallel to each other on a horizontal floor with a separation b between them. A wire of mass m lies on them perpendicularly, as shown in the figure. A vertically-upward magnetic field of strength B exists in the space. The metal strips are smooth but the coefficient of friction between the wire and the floor is µ. A current i is established when the switch S is closed at the instant t = 0. Discuss the motion of the wire after the switch is closed. How far away from the strips will the wire reach?
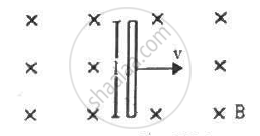
A conducting wire of length l, lying normal to a magnetic field B, moves with a velocity v,as shown in the figure. (a) Find the average magnetic force on a free electron of the wire. (b) Due to this magnetic force, electrons concentrate at one end, resulting in an electric field inside the wire. The redistribution stops when the electric force on the free electrons balances the magnetic force. Find the electric field developed inside the wire when the redistribution stops. (c) What potential difference is developed between the ends of the wire?
Answer the following question.
State the underlying principle of a cyclotron. Explain its working with the help of a schematic diagram. Obtain the expression for cyclotron frequency.
Cyclotron is used to ______.
Cyclotron frequency of a charged particle having charge q and mass m in a cyclotron producing magnetic field B is ______.
Assertion: The frequency of circular motion of a charged particle in cyclotron is independent of the mass of the particle.
Reason: Greater the mass of the particle less will be the frequency of the particle.
A charged particle is moving in a cyclotron, what effect on the radius of path of this charged particle will occur when the frequency of the ratio frequency field is doubled?
An aircraft executes a horizontal loop of radius 1.00 km with a steady speed of 900 km/h. Its centripetal acceleration is ______.
A particle of mass m is moving in a circular path of constant radius r such that, its centripetal acceleration ac is varying with time t as ac = k2rt2, where k is a constant. The power delivered to the particle by the forces acting on it is ______.
In a cyclotron, a charged particle ______.
