Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
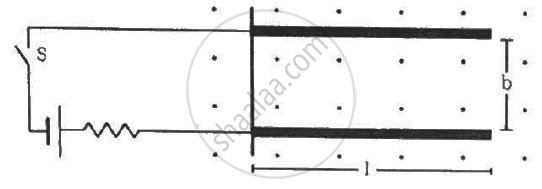
Two metal strips, each of length l, are clamped parallel to each other on a horizontal floor with a separation b between them. A wire of mass m lies on them perpendicularly, as shown in the figure. A vertically-upward magnetic field of strength B exists in the space. The metal strips are smooth but the coefficient of friction between the wire and the floor is µ. A current i is established when the switch S is closed at the instant t = 0. Discuss the motion of the wire after the switch is closed. How far away from the strips will the wire reach?
Solution
Given:-
Length of the two metal strips = l
Separation between the strips = b
Mass of the wire = m
Strength magnetic field = B
Coefficient of friction between the wire and the floor = µ
Let the distance covered by the wire be x.
Due to the presence of the magnetic field, a net magnetic force will act on the wire towards the right.
Let the wire has moved through a distance x after travelling the length of the strips.
As the contact between the wire and strip is smooth so coefficient of friction between them is zero. Under the influence of magnetic force,firstly the wire will travel a distance equal to the length of the strips. After this, it travels a distance x and also now,a frictional force will act on the wire in a direction opposite to its direction of motion.
So we can equate the work done by the magnetic force and the frictional force.
Thus, F × l = µmg × x,
where g is the acceleration due to gravity
⇒ ibBl = µmgx
⇒ `x = (iblB)/(mumg)`
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Draw a neat labelled diagram for the construction of 'cyclotron'
Which one of the following particles cannot be accelerated by a cyclotron?
(A) Electrons
(B) Protons
(C) Deuterons
(D) α- particles
State the principle of a cyclotron.
Show that the time period of revolution of particles in a cyclotron is independent of their speeds. Why is this property necessary for the operation of a cyclotron?
Deduce an expression for the frequency of revolution of a charged particle in a magnetic field and show that it is independent of velocity or energy of the particle.
A proton and an electron travelling along parallel paths enter a region of uniform magnetic field, acting perpendicular to their paths. Which of them will move in a circular path with higher frequency?
An α-particle and a proton are released from the centre of the cyclotron and made to accelerate.
(i) Can both be accelerated at the same cyclotron frequency?
Give reason to justify your answer.
(ii) When they are accelerated in turn, which of the two will have higher velocity at the exit slit of the does?
Verify that the units weber and volt second are the same.
Which of the following particles will describe the smallest circle when projected with the same velocity perpendicular to a magnetic field?
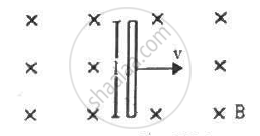
A conducting wire of length l, lying normal to a magnetic field B, moves with a velocity v,as shown in the figure. (a) Find the average magnetic force on a free electron of the wire. (b) Due to this magnetic force, electrons concentrate at one end, resulting in an electric field inside the wire. The redistribution stops when the electric force on the free electrons balances the magnetic force. Find the electric field developed inside the wire when the redistribution stops. (c) What potential difference is developed between the ends of the wire?
Answer the following question.
State the underlying principle of a cyclotron. Explain its working with the help of a schematic diagram. Obtain the expression for cyclotron frequency.
Cyclotron is used to ______.
A particle of mass m is moving in a circular path of constant radius r such that, its centripetal acceleration ac is varying with time t as ac = k2rt2, where k is a constant. The power delivered to the particle by the forces acting on it is ______.
In a cyclotron, a charged particle ______.
Describe the motion of a charged particle in a cyclotron if the frequency of the radio frequency (rf) field were doubled.
