Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Why is Butan-1-ol optically inactive but Butan-2-ol is optically active?
Solution
Butan-2-ol has a chiral centre, that is, butan-2-ol has a carbon atom bonded to four different substituents.
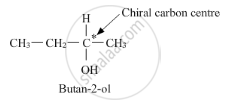
Thus, it is optically active. On the other hand, butan-1-ol does not have any chiral carbon atoms.
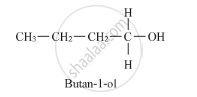
Therefore, it is optically inactive.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Draw the geometrical isomers of complex \[\ce{[Co(en)2Cl2]+}\].
Draw the structure of optical isomers of [Cr(C2O4)3]3−.
Draw the structure of optical isomers of [Cr(NH3)2Cl2(en)]+.
Draw all the isomers (geometrical and optical) of [CoCl2(en)2]+.
Draw all the isomers (geometrical and optical) of [Co(NH3)Cl(en)2]2+.
Name the type of isomerism shown by the following pair of compounds:
[CoCl(H2O)(NH3)4]Cl2 and [CoCl2(NH3)4]Cl.H2O
Write the IUPAC name of [Co(en)2Cl2]+ ion and draw the structures of its geometrical isomers.
The IUPAC name for [CoCl(NO2)(en)2]Cl is ____________.
The complex [(Pt(Py)(NH3)BrCl] will have how many geometrical isomers?
Assertion: Addition of bromine water to 1-butene gives two optical isomers.
Reason: The product formed contains two asymmetric carbon atoms.
