Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Why is it experimentally found difficult to detect neutrinos in this process ?
Solution
Neutrinos are difficult to detect experimentally in β-decay because they are uncharged particles with almost no mass. Also, as neutrinos interact very weakly with matter, therefore, they are very difficult to detect.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Why is it found experimentally difficult to detect neutrinos in nuclear β-decay?
The Q value of a nuclear reaction A + b → C + d is defined by
Q = [mA+ mb − mC − md]c2 where the masses refer to the respective nuclei. Determine from the given data the Q-value of the following reactions and state whether the reactions are exothermic or endothermic.
\[\ce{^12_6C + ^12_6C ->^20_10Ne + ^4_2He}\]
Atomic masses are given to be
`"m"(""_1^2"H")` = 2.014102 u
`"m"(""_1^3"H")` = 3.016049 u
`"m"(""_6^12C)` = 12.000000 u
`"m"(""_10^20"Ne")` = 19.992439 u
Under certain circumstances, a nucleus can decay by emitting a particle more massive than an α-particle. Consider the following decay processes:
\[\ce{^223_88Ra -> ^209_82Pb + ^14_6C}\]
\[\ce{^223_88 Ra -> ^219_86 Rn + ^4_2He}\]
Calculate the Q-values for these decays and determine that both are energetically allowed.
Calculate the maximum kinetic energy of the beta particle emitted in the following decay scheme:
12N → 12C* + e+ + v
12C* → 12C + γ (4.43MeV).
The atomic mass of 12N is 12.018613 u.
(Use Mass of proton mp = 1.007276 u, Mass of `""_1^1"H"` atom = 1.007825 u, Mass of neutron mn = 1.008665 u, Mass of electron = 0.0005486 u ≈ 511 keV/c2,1 u = 931 MeV/c2.)
The decay constant of 238U is 4.9 × 10−18 S−1. (a) What is the average-life of 238U? (b) What is the half-life of 238U? (c) By what factor does the activity of a 238U sample decrease in 9 × 109 years?
A radioactive substance disintegrates into two types of daughter nuclei, one type with disintegration constant λ1 and the other type with disintegration constant λ2 . Determine the half-life of the radioactive substance.
A radioactive element disintegrates for an interval of time equal to its mean lifetime. The fraction that has disintegrated is ______
If 10% of a radioactive material decay in 5 days, then the amount of original material left after 20 days is approximately :
The variation of decay rate of two radioactive samples A and B with time is shown in figure.
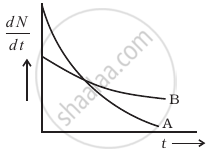
Which of the following statements are true?
- Decay constant of A is greater than that of B, hence A always decays faster than B.
- Decay constant of B is greater than that of A but its decay rate is always smaller than that of A.
- Decay constant of A is greater than that of B but it does not always decay faster than B.
- Decay constant of B is smaller than that of A but still its decay rate becomes equal to that of A at a later instant.
The activity R of an unknown radioactive nuclide is measured at hourly intervals. The results found are tabulated as follows:
| t (h) | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| R (MBq) | 100 | 35.36 | 12.51 | 4.42 | 1.56 |
- Plot the graph of R versus t and calculate the half-life from the graph.
- Plot the graph of ln `(R/R_0)` versus t and obtain the value of half-life from the graph.
