Advertisements
Advertisements
Questions
Write the reaction involved when D-glucose is treated with the following reagent:
Br2 water
What happens when D-glucose is treated with the following reagent?
Bromine water
Solution
When glucose is heated with bromine water, it is oxidised to gluconic acid, a six-carbon carboxylic acid.
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\phantom{........}\ce{CHO}\phantom{.............}\ce{COOH}\phantom{..}\\
\phantom{.}|\phantom{..................}|\\
\phantom{.......}\ce{(CHOH)4->[Br2 water](CHOH)4}\\
\phantom{.}|\phantom{..................}|\\
\phantom{.............}\ce{\underset{\text{D-glucose}}{CH2OH}}\phantom{........}\ce{\underset{\text{D-gluconic acid}}{CH2OH}}\phantom{.}
\end{array}\]
RELATED QUESTIONS
Write the product when D-glucose reacts with conc. HNO3.
Differentiable between the following:
Amylose and Amylopectin
Answer the following question.
What is the basic structural difference between glucose and fructose?
The spatial arrangement of the given molecule is denoted by:

The number of asymmetric carbon atom(s) below the figure is/are

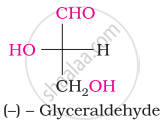
Glucose does not react with ____________.
Which of the following properties of glucose cannot be explained by its open chain structure?
(i) Glucose does not form hydrogen sulphite with NaHSO3.
(ii) On oxidation with HNO3 glucose gives saccharic acid.
(iii) Glucose is found to exist in two different crystalline forms which are named as α and β.
Which is the least stable form of glucose?
A solution of D-glucose in water rotates the plane polarised light ____________.
The number of chiral carbon atoms present in cyclic structure α-D(+) glucose:
The letter D and L in carbohydrates represent ____________.
Which one is correct?
Which of the following pairs represents anomers?
Three structures are given below in which two glucose units are linked. Which of these linkages between glucose units are between C1 and C4 and which linkages are between C1 and C6?
| (I) |  |
| (II) | 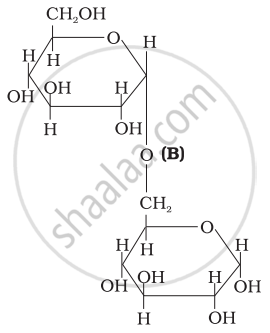 |
| (III) | 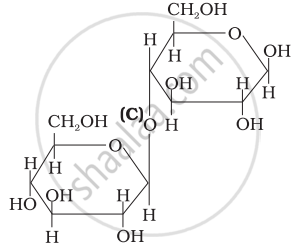 |
How will you distinguish 1° and 2° hydroxyl groups present in glucose? Explain with reactions.
Consider the following reactions:
(i) \[\ce{Glucose + R-OH ->[Conc. HNO3] [A] ->[X eq of][(CH3CO)2O] Acetyl derivative}\]
(ii) \[\ce{Glucose ->[Ni/H2] [A] ->[Y eq of][(CH3CO)2O] Acetyl derivative}\]
(iii) \[\ce{Glucose ->[Z eq of][(CH3CO)2O] Acetyl derivative}\]
'X, 'Y' and 'Z' in these reactions are respectively:
When D-glucose reacts with HI, it forms ______.
